Effect of an inhibitor of Jun N-terminal protein kinase, SP600125, in single allergen challenge in sensitized rats
- PMID: 15196213
- PMCID: PMC1782503
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01887.x
Effect of an inhibitor of Jun N-terminal protein kinase, SP600125, in single allergen challenge in sensitized rats
Abstract
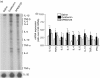
Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases including asthma. We examined the effect of SP600125 (anthra [1,9-cd] pyrazol-6 (2H)-one), a novel inhibitor of JNK in a model of asthma. Brown-Norway rats were sensitized to ovalbumin and treated with SP600125 intraperitoneally (90 mg/kg in total). SP600125 inhibited allergen-induced, increased activity of phosphorylated c-jun but not of phosphorylated-MAPKAPK2, indicative of activation of p38 MAPK, in the lung. SP600125 inhibited macrophage (P < 0.04), lymphocyte (P < 0.05), eosinophil (P < 0.04) and neutrophil (P < 0.005) numbers in bronchoalveolar lavage. Eosinophil and T-cell accumulation in the airways, mRNA expression for interleukin-1beta, tumour necrosis factor-beta, interleukin-3, interleukin-4 and interleukin-5, serum levels of allergen-specific immunoglobulin E and bronchial hyperresponsiveness were not affected by SP600125. Selective inhibition of JNK reduced inflammatory cell egress into the airway lumen after single allergen exposure. The role of JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase activation may be limited in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness after single allergen exposure.
Figures

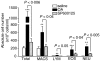


Similar articles
-
Potential role of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in allergic airway inflammation and remodelling: effects of SP600125.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Jan 4;506(3):273-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.11.040. Epub 2004 Dec 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15627438
-
SP600125 promotes resolution of allergic airway inflammation via TLR9 in an OVA-induced murine acute asthma model.Mol Immunol. 2015 Oct;67(2 Pt B):311-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26139014
-
Allergen-induced inflammation and airway epithelial and smooth muscle cell proliferation: role of Jun N-terminal kinase.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;140(8):1373-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705569. Epub 2003 Nov 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14623764 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of ozone-induced airway inflammation and hyper-responsiveness by c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jul;322(1):351-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.121624. Epub 2007 Apr 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17460151
-
A novel transcription factor inhibitor, SP100030, inhibits cytokine gene expression, but not airway eosinophilia or hyperresponsiveness in sensitized and allergen-exposed rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Nov;134(5):1029-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704344. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11682451 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Histamine H1 Receptor-Mediated JNK Phosphorylation Is Regulated by Gq Protein-Dependent but Arrestin-Independent Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 17;25(6):3395. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063395. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542369 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in MAP kinase phosphorylation in response to mechanical strain in asthmatic fibroblasts.Respir Res. 2006 Apr 27;7(1):68. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-68. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16643666 Free PMC article.
-
TEC and MAPK Kinase Signalling Pathways in T helper (TH) cell Development, TH2 Differentiation and Allergic Asthma.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2012;Suppl 12:11. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.S12-011. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2012. PMID: 24116341 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase inhibitors: where are we now and where are we going?Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Nov;65 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):iii83-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.058388. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 17038480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of C-Jun N-terminal Kinase in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development.Target Oncol. 2016 Dec;11(6):723-738. doi: 10.1007/s11523-016-0446-5. Target Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27392951 Review.
References
-
- Robinson DS, Hamid Q, Ying S, et al. Predominant Th2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Huang TJ, Macary PA, Eynott P, et al. Allergen-specific Th1 cells counteract efferent Th2 cell-dependent bronchial hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilic inflammation partly via IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 2001;166:207–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
