Cutaneous infections of mice with vaccinia or cowpox viruses and efficacy of cidofovir
- PMID: 15196818
- PMCID: PMC9528221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2004.02.003
Cutaneous infections of mice with vaccinia or cowpox viruses and efficacy of cidofovir
Abstract
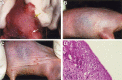
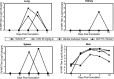
Orthopoxviruses, including smallpox, monkeypox and molluscipox, pose risks to human health through bioterrorist acts or natural transmission. There is no approved therapy for orthopoxvirus infections; however, cidofovir (CDV) has been approved as an investigational new drug for emergency treatment of adverse effects following smallpox vaccination. For evaluation of new therapies directed against orthopoxvirus infections, we have utilized immunocompetent, hairless mice (SKH-1) inoculated by a cutaneous route with cowpox virus (CV) or vaccinia virus (VV). Mice subsequently developed skin lesions and virus was recovered from the site of inoculation and quantified. Skin biopsies were evaluated microscopically, revealing brick-like eosinophilic, intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies characteristic of orthopoxvirus infection. SKH-1 mice fully recovered from either CV or VV infection. Immunodeficient Athymic or Rhino mice inoculated with CV or VV had more lesions and severe disease than SKH-1 mice. CV-infected SKH-1 mice were treated either with systemic or topical CDV. Although some protection was achieved with systemic treatment, 5% topical CDV was most effective at reducing virus titers in skin, lung, kidney, and spleen. These models may provide a means for evaluating efficacy of new therapies directed against orthopoxvirus diseases and further confirm the topical activity of CDV against cutaneous infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of multiple- or single-dose cidofovir against vaccinia and cowpox virus infections in mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Oct;47(10):3275-80. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.10.3275-3280.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 14506041 Free PMC article.
-
Oral treatment of cowpox and vaccinia virus infections in mice with ether lipid esters of cidofovir.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Feb;48(2):404-12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.2.404-412.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 14742188 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of cidofovir and cyclic HPMPC on lethal cowpox and vaccinia virus respiratory infections in mice.Chemotherapy. 2003 Jun;49(3):126-31. doi: 10.1159/000070618. Chemotherapy. 2003. PMID: 12815205
-
In vitro activity of potential anti-poxvirus agents.Antiviral Res. 2003 Jan;57(1-2):35-40. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(02)00198-5. Antiviral Res. 2003. PMID: 12615301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the discovery of compounds inhibiting orthopoxviruses in animal models.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2008;19(3):115-24. doi: 10.1177/095632020801900302. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2008. PMID: 19024628 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of Vaccinia and Cowpox Virus Infections in Mice with CMX001 and ST-246.Viruses. 2010 Dec;2(12):2681-95. doi: 10.3390/v2122681. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994637 Free PMC article.
-
Orthopoxvirus targets for the development of new antiviral agents.Antiviral Res. 2012 May;94(2):111-25. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Antiviral Res. 2012. PMID: 22406470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of imiquimod for topical treatment of vaccinia virus cutaneous infections in immunosuppressed hairless mice.Antiviral Res. 2011 Jun;90(3):126-33. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.03.181. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 21439326 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of herpesvirus replication by hexadecyloxypropyl esters of purine- and pyrimidine-based phosphonomethoxyethyl nucleoside phosphonates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Dec;52(12):4326-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00918-08. Epub 2008 Oct 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18852272 Free PMC article.
-
Cowpox Virus: A New and Armed Oncolytic Poxvirus.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2017 Aug 24;7:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2017.08.003. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2017. PMID: 28951885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bienvenu B, Martinez F, Devergie A, Rybojad M, Rivet J, Bellenger P, Morel P, Gluckman E, Lebbe C. Topical use of cidofovir induced acute renal failure. Transplantation. 2002;73:661–662. - PubMed
-
- Boyle J.J, Haff R.F, Stewart R.C. Evaluation of antiviral compounds by suppression of tail lesions in vaccinia-infected mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967;6:536–539. - PubMed
-
- Bray M, Martinez M, Smee D.F, Kefauver D, Thompson E, Huggins J.W. Cidofovir protects mice against lethal aerosol or intranasal cowpox virus challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2000;181:10–19. - PubMed
-
- Buller R.M.L. The BALB/c mouse as a model to study orthopoxviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1985;122:148–153. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2003a. Multistate outbreak of monkeypox—Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin, 2003. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 52, 537–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

