Nicotine blocks apomorphine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats: possible involvement of central nicotinic alpha7 receptors
- PMID: 15197106
- PMCID: PMC1575066
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705855
Nicotine blocks apomorphine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats: possible involvement of central nicotinic alpha7 receptors
Abstract
Nicotine has been reported to normalize deficits in auditory sensory gating in the cases of schizophrenia, suggesting an involvement of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in attentional abnormalities. However, the mechanism remains unclear. The present study investigated the effects of nicotine on the disruption of prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response induced by apomorphine or phencyclidine in rats. Over the dose range tested, nicotine (0.05-1 mg kg(-1), s.c.) did not disrupt PPI. Neither methyllycaconitine (0.5-5 mg kg(-1), s.c.), an alpha(7) nicotinic receptor antagonist, nor dihydro-beta-erythroidine (0.5-2 mg kg(-1), s.c.), an alpha(4)beta(2) nicotinic receptor antagonist, had any effect on PPI. Nicotine (0.01-0.2 mg kg(-1), s.c.) dose-dependently reversed the disruption of PPI induced by apomorphine (1 mg kg(-1), s.c.), but had no effect on the disruption of PPI induced by phencyclidine (2 mg kg(-1), s.c.). The reversal of apomorphine-induced PPI disruption by nicotine (0.2 mg kg(-1)) was eliminated by mecamylamine (1 mg kg(-1), i.p.), but not by hexamethonium (10 mg kg(-1), i.p.), indicating the involvement of central nicotinic receptors. The antagonistic action of nicotine on apomorphine-induced PPI disruption was dose-dependently blocked by methyllycaconitine (1 and 2 mg kg(-1), s.c.). However, dihydro-beta-erythroidine (1 and 2 mg kg(-1), s.c.) had no effect. These results suggest that nicotine reverses the disruption of apomorphine-induced PPI through central alpha(7) nicotinic receptors.
Figures
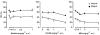
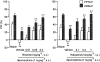
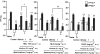
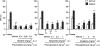
Similar articles
-
Effects of the nicotinic α7 receptor partial agonist GTS-21 on NMDA-glutamatergic receptor related deficits in sensorimotor gating and recognition memory in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(18):3695-706. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3509-2. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24595504 Free PMC article.
-
Varenicline disrupts prepulse inhibition only in high-inhibitory rats.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Aug 4;53:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24632394
-
Role of nicotinic receptors in the lateral habenula in the attenuation of amphetamine-induced prepulse inhibition deficits of the acoustic startle response in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(16):3009-17. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3940-z. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25912180 Free PMC article.
-
[Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are possible therapeutic targets for schizophrenia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009 Feb;129(2):197-201. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.129.197. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19182447 Review. Japanese.
-
Nicotinic mechanisms in the treatment of psychotic disorders: a focus on the α7 nicotinic receptor.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012;(213):211-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-25758-2_8. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23027417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Behavioral assessment of rimonabant under acute and chronic conditions.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jul 15;390:112697. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112697. Epub 2020 May 15. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32417279 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine effect on prepulse inhibition and prepulse facilitation in schizophrenia patients.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Aug;33(9):2167-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301601. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 17957213 Free PMC article.
-
Treating schizophrenia symptoms with an alpha7 nicotinic agonist, from mice to men.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 15;74(8):1192-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.015. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17714692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the MATRICS to guide development of a preclinical cognitive test battery for research in schizophrenia.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 May;122(2):150-202. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.02.004. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19269307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotine and nicotinic system in hypoglutamatergic models of schizophrenia.Neurotox Res. 2007 Dec;12(4):233-46. doi: 10.1007/BF03033907. Neurotox Res. 2007. PMID: 18201951 Review.
References
-
- ABDULJAWAD K.A., LANGLEY R.W., BRADSHAW C.M., SZABADI E. Effects of clonidine and diazepam on the acoustic startle response and on its inhibition by ‘prepulse' in man. J. Psychopharmacol. 1997;11:29–34. - PubMed
-
- ACRI J.B., MORSE D.E., POPKE E.J., GRUNBERG N.E. Nicotine increases sensory gating measured as inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology. 1994;114:369–374. - PubMed
-
- ACRI J.B., BROWN K.J., SAAH M.I., GRUNBERG N.E. Strain and age differences in acoustic startle responses and effects of nicotine in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995;50:191–198. - PubMed
-
- ADLER L.E., HOFFER L.J., GRIFFITH J., WALDO M.C., FREEDMAN R. Normalization by nicotine of deficient auditory sensory gating in the relatives of schizophrenics. Biol. Psychiatry. 1992;32:607–616. - PubMed
-
- ADLER L.E., HOFFER L.D., WISER A., FREEDMAN R. Normalization of auditory physiology by cigarette smoking in schizophrenic patients. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1993;150:1856–1861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

