Molecular pharmacological profile of the nonredox-type 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor CJ-13,610
- PMID: 15197110
- PMCID: PMC1575070
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705860
Molecular pharmacological profile of the nonredox-type 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor CJ-13,610
Abstract
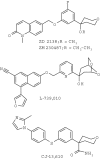
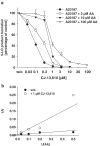
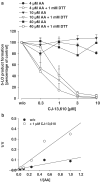
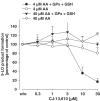
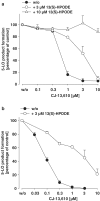
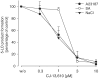
5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is a crucial enzyme in the synthesis of the bioactive leukotrienes (LTs) from arachidonic acid (AA), and inhibitors of 5-LO are thought to prevent the untowarded pathophysiological effects of LTs. In this study, we present the molecular pharmacological profile of the novel nonredox-type 5-LO inhibitor CJ-13,610 that was evaluated in various in vitro assays. In intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL), challenged with the Ca(2+)-ionophore A23187, CJ-13,610 potently suppressed 5-LO product formation with an IC(50)=0.07 microm. Supplementation of exogenous AA impaired the efficacy of CJ-13,610, implying a competitive mode of action. In analogy to ZM230487 and L-739.010, two closely related nonredox-type 5-LO inhibitors, CJ-13,610 up to 30 microm failed to inhibit 5-LO in cell-free assay systems under nonreducing conditions, but inclusion of peroxidase activity restored the efficacy of CJ-13,610 (IC(50)=0.3 microm). In contrast to ZM230487 and L-739.010, the potency of CJ-13,610 does not depend on the cell stimulus or the activation pathway of 5-LO. Thus, 5-LO product formation in PMNL induced by phosphorylation events was equally suppressed by CJ-13,610 as compared to Ca(2+)-mediated 5-LO activation. In transfected HeLa cells, CJ-13,610 only slightly discriminated between phosphorylatable wild-type 5-LO and a 5-LO mutant that lacks phosphorylation sites. In summary, CJ-13,610 may possess considerable potential as a potent orally active nonredox-type 5-LO inhibitor that lacks certain disadvantages of former representatives of this class of 5-LO inhibitors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation- and stimulus-dependent inhibition of cellular 5-lipoxygenase activity by nonredox-type inhibitors.FASEB J. 2003 May;17(8):949-51. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0815fje. Epub 2003 Mar 28. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 12670876
-
Molecular characterization of EP6--a novel imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine based direct 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jan 15;83(2):228-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22027220
-
The molecular mechanism of the inhibition by licofelone of the biosynthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;152(4):471-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707416. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17704828 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the search for novel 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Jan;114(1):70-7. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12114. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 23953428 Review.
-
5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors: a review of recent patents (2010-2012).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2013 Jul;23(7):895-909. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2013.791678. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2013. PMID: 23600432 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the role of lipoxygenase and its inhibitors in prostate cancer.Future Oncol. 2024 Dec;20(40):3549-3568. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2419356. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39535136 Review.
-
On the inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase product formation by tryptanthrin: mechanistic studies and efficacy in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(3):765-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01605.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21797843 Free PMC article.
-
The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14: enzymes.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(8):1797-867. doi: 10.1111/bph.12451. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24528243 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the molecular mechanism and the efficacy in vivo of a novel 1,4-benzoquinone that inhibits 5-lipoxygenase.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 May;171(9):2399-412. doi: 10.1111/bph.12592. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24467325 Free PMC article.
-
The novel benzimidazole derivative BRP-7 inhibits leukotriene biosynthesis in vitro and in vivo by targeting 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP).Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;171(12):3051-64. doi: 10.1111/bph.12625. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24641614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALANKO J., SIEVI E., LAHTEENMAKI T., MUCHA I., VAPAATALO H., PARANTAINEN J. Catechol estrogens as inhibitors of leukotriene synthesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998;55:101–104. - PubMed
-
- BURKERT E., SZELLAS D., RADMARK O., STEINHILBER D., WERZ O. Cell type-dependent activation of 5-lipoxygenase by arachidonic acid. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2003;73:191–200. - PubMed
-
- CHEN X.S., SHELLER J.R., JOHNSON E.N., FUNK C.D. Role of leukotrienes revealed by targeted disruption of the 5-lipoxygenase gene. Nature. 1994;372:179–182. - PubMed
-
- CLAESSON H.E., DAHLEN S.E. Asthma and leukotrienes: antileukotrienes as novel anti-asthmatic drugs. J. Intern. Med. 1999;245:205–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

