Unique inner pore properties of BK channels revealed by quaternary ammonium block
- PMID: 15197222
- PMCID: PMC2229608
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200409067
Unique inner pore properties of BK channels revealed by quaternary ammonium block
Abstract
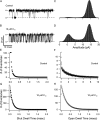
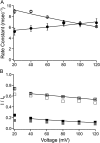
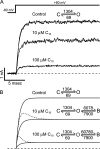
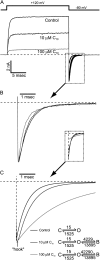
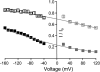
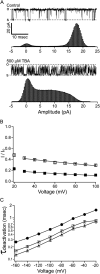
Potassium channels have a very wide distribution of single-channel conductance, with BK type Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels having by far the largest. Even though crystallographic views of K(+) channel pores have become available, the structural basis underlying BK channels' large conductance has not been completely understood. In this study we use intracellularly applied quaternary ammonium compounds to probe the pore of BK channels. We show that molecules as large as decyltriethylammonium (C(10)) and tetrabutylammonium (TBA) have much faster block and unblock rates in BK channels when compared with any other tested K(+) channel types. Additionally, our results suggest that at repolarization large QA molecules may be trapped inside blocked BK channels without slowing the overall process of deactivation. Based on these findings we propose that BK channels may differ from other K(+) channels in its geometrical design at the inner mouth, with an enlarged cavity and inner pore providing less spatially restricted access to the cytoplasmic solution. These features could potentially contribute to the large conductance of BK channels.
Figures




Similar articles
-
State-dependent block of BK channels by synthesized shaker ball peptides.J Gen Physiol. 2006 Oct;128(4):423-41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200609521. Epub 2006 Sep 11. J Gen Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16966472 Free PMC article.
-
State-independent block of BK channels by an intracellular quaternary ammonium.J Gen Physiol. 2006 Sep;128(3):347-64. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200609579. J Gen Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16940557 Free PMC article.
-
Novel alpha-KTx sites in the BK channel and comparative sequence analysis reveal distinguishing features of the BK and KV channel outer pore.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2008;52(1):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s12013-008-9026-3. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18815746
-
Large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels: structural and functional implications.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Apr;110(1):103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.10.007. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16356551 Review.
-
Modulation of calcium-activated potassium channels.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2002 Mar;188(2):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s00359-002-0281-2. Epub 2002 Jan 29. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11919690 Review.
Cited by
-
The BK channel: a vital link between cellular calcium and electrical signaling.Protein Cell. 2012 Dec;3(12):883-92. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2076-8. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Protein Cell. 2012. PMID: 22996175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the mechanism of TBA block of the TRPV1 channel.Biophys J. 2007 Jun 1;92(11):3901-14. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.102400. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17369424 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid intracellular TEA block of the KcsA potassium channel.Biophys J. 2005 Feb;88(2):1018-29. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.052043. Epub 2004 Nov 19. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15556975 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of ion permeation gating in Slo2.1 K+ channels.J Gen Physiol. 2013 Nov;142(5):523-42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201311064. J Gen Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24166878 Free PMC article.
-
Low resistance, large dimension entrance to the inner cavity of BK channels determined by changing side-chain volume.J Gen Physiol. 2011 Jun;137(6):533-48. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201110616. Epub 2011 May 16. J Gen Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21576375 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

