Spindle checkpoint regulates Cdc20p stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 15198982
- PMCID: PMC423194
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1184204
Spindle checkpoint regulates Cdc20p stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
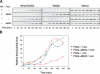
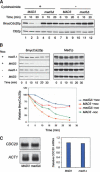
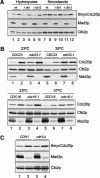
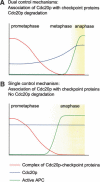
The spindle checkpoint arrests cells at the metaphase-to-anaphase transition until all chromosomes have properly attached to the mitotic spindle. Checkpoint proteins Mad2p and Mad3p/BubR1p bind and inhibit Cdc20p, an activator for the anaphase-promoting complex (APC). We find that upon spindle checkpoint activation by microtubule inhibitors benomyl or nocodazole, wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains less Cdc20p than spindle checkpoint mutants do, whereas their CDC20 mRNA levels are similar. The difference in Cdc20p levels correlates with their difference in the half-lives of Cdc20p, indicating that the spindle checkpoint destabilizes Cdc20p. This process requires the association between Cdc20p and Mad2p, and functional APC, but is independent of the known destruction boxes in Cdc20p and the other APC activator Cdh1p. Importantly, destabilization of Cdc20p is important for the spindle checkpoint, because a modest overexpression of Cdc20p causes benomyl sensitivity and premature Pds1p degradation in cells treated with nocodazole. Our study suggests that the spindle checkpoint reduces Cdc20p to below a certain threshold level to ensure a complete inhibition of Cdc20p before anaphase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mad3p, a pseudosubstrate inhibitor of APCCdc20 in the spindle assembly checkpoint.Genes Dev. 2007 Mar 15;21(6):655-67. doi: 10.1101/gad.1511107. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17369399 Free PMC article.
-
Mad3 KEN boxes mediate both Cdc20 and Mad3 turnover, and are critical for the spindle checkpoint.PLoS One. 2007 Apr 4;2(4):e342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000342. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17406666 Free PMC article.
-
The Polo-like kinase Cdc5p and the WD-repeat protein Cdc20p/fizzy are regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 1998 Mar 2;17(5):1336-49. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1336. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9482731 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of APC-Cdc20 by the spindle checkpoint.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;14(6):706-14. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(02)00382-4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12473343 Review.
-
Dual inhibition of Cdc20 by the spindle checkpoint.J Biomed Sci. 2007 Jul;14(4):475-9. doi: 10.1007/s11373-007-9157-3. Epub 2007 Mar 17. J Biomed Sci. 2007. PMID: 17370142 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms creating bistable switches at cell cycle transitions.Open Biol. 2013 Mar 13;3(3):120179. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120179. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23486222 Free PMC article.
-
Cubism and the cell cycle: the many faces of the APC/C.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 2;12(7):427-38. doi: 10.1038/nrm3132. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21633387 Review.
-
Cell cycle regulation of condensin Smc4.Oncotarget. 2019 Jan 8;10(3):263-276. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26467. eCollection 2019 Jan 8. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30719224 Free PMC article.
-
Non-proteolytic ubiquitylation counteracts the APC/C-inhibitory function of XErp1.EMBO Rep. 2011 May;12(5):436-43. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.32. Epub 2011 Mar 11. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21399619 Free PMC article.
-
Spindle checkpoint silencing: ensuring rapid and concerted anaphase onset.F1000 Biol Rep. 2010 Jul 22;2:55. doi: 10.3410/B2-55. F1000 Biol Rep. 2010. PMID: 21173869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, B.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. 2000. Current protocols in molecular biology, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
-
- Clarke D.J., Segal, M., Andrews, C.A., Rudyak, S.G., Jensen, S., Smith, K., and Reed, S.I. 2003. S-Phase checkpoint controls mitosis via an APC-independent Cdc20p function. Nat. Cell Biol. 5: 928-935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
