Distinct mechanisms for repression of RNA polymerase III transcription by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein
- PMID: 15199152
- PMCID: PMC480882
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5989-5999.2004
Distinct mechanisms for repression of RNA polymerase III transcription by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein
Abstract
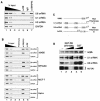
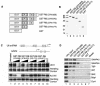
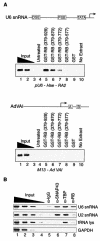
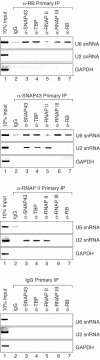
The retinoblastoma (RB) protein represses global RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that encode nontranslated RNAs, potentially to control cell growth. However, RNA polymerase III-transcribed genes exhibit diverse promoter structures and factor requirements for transcription, and a universal mechanism explaining global repression is uncertain. We show that RB represses different classes of RNA polymerase III-transcribed genes via distinct mechanisms. Repression of human U6 snRNA (class 3) gene transcription occurs through stable promoter occupancy by RB, whereas repression of adenovirus VAI (class 2) gene transcription occurs in the absence of detectable RB-promoter association. Endogenous RB binds to a human U6 snRNA gene in both normal and cancer cells that maintain functional RB but not in HeLa cells whose RB function is disrupted by the papillomavirus E7 protein. Both U6 promoter association and transcriptional repression require the A/B pocket domain and C region of RB. These regions of RB contribute to U6 promoter targeting through numerous interactions with components of the U6 general transcription machinery, including SNAP(C) and TFIIIB. Importantly, RB also concurrently occupies a U6 promoter with RNA polymerase III during repression. These observations suggest a novel mechanism for RB function wherein RB can repress U6 transcription at critical steps subsequent to RNA polymerase III recruitment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein targets distinct general transcription factors to regulate RNA polymerase III gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(24):9182-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9182-9191.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11094070 Free PMC article.
-
The p53 tumor suppressor protein represses human snRNA gene transcription by RNA polymerases II and III independently of sequence-specific DNA binding.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3247-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3247-3260.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798209 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RNA polymerase III transcription by BRCA1.J Mol Biol. 2009 Apr 3;387(3):523-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.02.008. Epub 2009 Feb 11. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19361418
-
RNA polymerase III repression by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.09.011. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23063750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription and cancer.Oncogene. 2004 Apr 19;23(18):3208-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207547. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15094770 Review.
Cited by
-
RNF12 catalyzes BRF1 ubiquitination and regulates RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 4;294(1):130-141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004524. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30413534 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription is required for oncogenic transformation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 11;283(28):19184-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802872200. Epub 2008 May 1. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18456653 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Drosophila RBf2 Protein Highlights the Diversity of RB Family Targets and Possible Role in Regulation of Ribosome Biosynthesis.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 May 20;5(7):1503-15. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.019166. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 25999584 Free PMC article.
-
The JNKs differentially regulate RNA polymerase III transcription by coordinately modulating the expression of all TFIIIB subunits.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 4;106(31):12682-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904843106. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19620725 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal expression of TFIIIB subunits and RNA Pol III genes is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Res. 2017 Sep;1(2):112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Liver Res. 2017. PMID: 29276645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braunstein, M., A. B. Rose, S. G. Holmes, C. D. Allis, and J. R. Broach. 1993. Transcriptional silencing in yeast is associated with reduced nucleosome acetylation. Genes Dev. 7:592-604. - PubMed
-
- Brehm, A., E. A. Miska, D. J. McCance, J. L. Reid, A. J. Bannister, and T. Kouzarides. 1998. Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature 391:597-601. - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh, A. H., W. M. Hempel, L. J. Taylor, V. Rogalsky, G. Todorov, and L. I. Rothblum. 1995. Activity of RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF blocked by Rb gene product. Nature 374:177-180. - PubMed
-
- Chellappan, S. P., S. Hiebert, M. Mudryj, J. M. Horowitz, and J. R. Nevins. 1991. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell 65:1053-1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
