Sensing complex regulatory networks by conformationally controlled hairpin ribozymes
- PMID: 15199169
- PMCID: PMC434448
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh643
Sensing complex regulatory networks by conformationally controlled hairpin ribozymes
Abstract
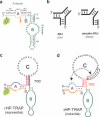
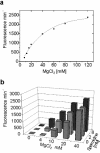
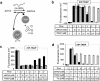
The hairpin ribozyme catalyses RNA cleavage by a mechanism utilizing its conformational flexibility during the docking of two independently folded internal loop domains A and B. Based on this mechanism, we designed hairpin ribozyme variants that can be induced or repressed by external effector oligonucleotides influencing the docking process. We incorporated a third domain C to assimilate alternate stable RNA motifs such as a pseudo-half-knot or an internal stem-loop structure. Small sequence changes in domain C allowed targeted switching of ribozyme activity: the same effector oligonucleotide can either serve as an inducer or repressor. The ribozymes were applied to trp leader mRNA, the RNA sequence tightly bound by l-tryptophan-activated trp-RNA-binding attenuation protein (TRAP). When domain C is complementary to this mRNA, ribozyme activity can be altered by annealing trp leader mRNA, then specifically reverted by its TRAP/tryptophan-mediated sequestration. This approach allows to precisely sense the activity status of a protein controlled by its metabolite molecule.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Competitive regulation of modular allosteric aptazymes by a small molecule and oligonucleotide effector.RNA. 2005 Oct;11(10):1514-20. doi: 10.1261/rna.2840805. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16199761 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro selection of hairpin ribozymes activated with short oligonucleotides.Biochemistry. 2002 Jul 23;41(29):9090-8. doi: 10.1021/bi020012s. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12119023
-
Construction of new ribozymes requiring short regulator oligonucleotides as a cofactor.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jun 23;299(5):1231-43. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3825. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10873448
-
The many faces of the hairpin ribozyme: structural and functional variants of a small catalytic RNA.IUBMB Life. 2012 Jan;64(1):36-47. doi: 10.1002/iub.575. Epub 2011 Nov 30. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22131309 Review.
-
Regulation of ribozyme activity with short oligonucleotides.Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 Apr;27(4):457-62. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.457. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004. PMID: 15056847 Review.
Cited by
-
MIPs and Aptamers for Recognition of Proteins in Biomimetic Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2016 Jul 18;6(3):35. doi: 10.3390/bios6030035. Biosensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27438862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Competitive regulation of modular allosteric aptazymes by a small molecule and oligonucleotide effector.RNA. 2005 Oct;11(10):1514-20. doi: 10.1261/rna.2840805. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16199761 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of Small Ribozymes Acting on RNA: What is Needed to Make a New Function Work with an Existing Catalyst?Chembiochem. 2025 May 27;26(10):e202500213. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500213. Epub 2025 May 21. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40295187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deoxyribozymes that recode sequence information.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Apr 28;34(8):2166-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl176. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16648360 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamers for allosteric regulation.Nat Chem Biol. 2011 Jul 18;7(8):519-27. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.609. Nat Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21769099 Review.
References
-
- Doudna J.A. and Cech,T.R. (2002) The chemical repertoire of natural ribozymes. Nature, 418, 222–228. - PubMed
-
- Butcher S.E. (2001) Structure and function of the small ribozymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 11, 315–320. - PubMed
-
- Ferre-D'amare A.R. and Rupert,P.B. (2002) The hairpin ribozyme: from crystal structure to function. Biochem. Soc. Trans., 30, 1105–1109. - PubMed
-
- Hampel K.J., Pinard,R. and Burke,J.M. (2001) Catalytic and structural assays for the hairpin ribozyme. Methods Enzymol., 341, 566–580. - PubMed
-
- Esteban J.A., Banerjee,A.R. and Burke,J.M. (1997) Kinetic mechanism of the hairpin ribozyme. Identification and characterization of two nonexchangeable conformations. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 13629–13639. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

