The recognition and modification sites for the bacterial type I restriction systems KpnAI, StySEAI, StySENI and StySGI
- PMID: 15199175
- PMCID: PMC434458
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh079
The recognition and modification sites for the bacterial type I restriction systems KpnAI, StySEAI, StySENI and StySGI
Abstract
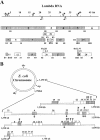
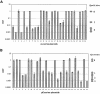
Using an in vivo plasmid transformation method, we have determined the DNA sequences recognized by the KpnAI, StySEAI, StySENI and StySGI R-M systems from Klebsiella oxytoca strain M5a1, Salmonella eastbourne, Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella gelsenkirchen, respectively. These type I restriction-modification systems were originally identified using traditional phage assay, and described here is the plasmid transformation test and computer program used to determine their DNA recognition sequences. For this test, we constructed two sets of plasmids, pL and pE, that contain phage lambda and Escherichia coli K-12 chromosomal DNA fragments, respectively. Further, using the methylation sensitivities of various known type II restriction enzymes, we identified the target adenines for methylation (listed in bold italics below as A or T in case of the complementary strand). The recognition sequence and methylation sites are GAA(6N)TGCC (KpnAI), ACA(6N)TYCA (StySEAI), CGA(6N)TACC (StySENI) and TAAC(7N)RTCG (StySGI). These DNA recognition sequences all have a typical type I bipartite pattern and represent three novel specificities and one isoschizomer (StySENI). For confirmation, oligonucleotides containing each of the predicted sequences were synthesized, cloned into plasmid pMECA and transformed into each strain, resulting in a large reduction in efficiency of transformation (EOT).
Figures
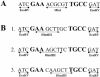


Similar articles
-
KpnBI is the prototype of a new family (IE) of bacterial type I restriction-modification system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Oct 8;32(18):e138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh134. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15475385 Free PMC article.
-
Four new type I restriction enzymes identified in Escherichia coli clinical isolates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 21;33(13):e114. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni114. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16040596 Free PMC article.
-
KpnAI, a new type I restriction-modification system in Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Mol Biol. 1997 Aug 22;271(3):342-8. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1202. J Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9268663
-
[Antirestriction proteins ardA and Ocr as effective inhibitors of the type I restriction-modification enzymes].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009 Mar-Apr;43(2):264-73. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009. PMID: 19425495 Review. Russian.
-
Defining domains in type-I restriction and modification enzymes.Gene. 1988 Dec 25;74(1):239-41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90295-8. Gene. 1988. PMID: 3074012 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Quick identification of Type I restriction enzyme isoschizomers using newly developed pTypeI and reference plasmids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Aug;36(13):e81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn056. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18562466 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a restriction modification system from the commensal Escherichia coli strain A0 34/86 (O83:K24:H31).BMC Microbiol. 2008 Jun 27;8:106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-106. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18588664 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights of the DNA cutters: a short history of the restriction enzymes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):3-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt990. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24141096 Free PMC article.
-
KpnBI is the prototype of a new family (IE) of bacterial type I restriction-modification system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Oct 8;32(18):e138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh134. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15475385 Free PMC article.
-
Type I restriction enzymes and their relatives.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):20-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt847. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24068554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nagaraja V., Shepherd,J.C., Pripfl,T. and Bickle,T.A. (1985) Two type I restriction enzymes from Salmonella species. Purification and DNA recognition sequences. J. Mol. Biol., 182, 579–587. - PubMed
-
- Cowan G.M., Gann,A.A. and Murray,N.E. (1989) Conservation of complex DNA recognition domains between families of restriction enzymes. Cell, 56, 103–109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

