Disruption of Fgf10/Fgfr2b-coordinated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions causes cleft palate
- PMID: 15199404
- PMCID: PMC420504
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20384
Disruption of Fgf10/Fgfr2b-coordinated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions causes cleft palate
Abstract
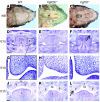
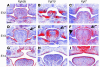
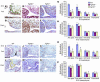
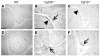
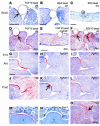
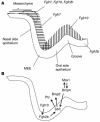
Classical research has suggested that early palate formation develops via epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, and in this study we reveal which signals control this process. Using Fgf10-/-, FGF receptor 2b-/- (Fgfr2b-/-), and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) mutant mice, which all exhibit cleft palate, we show that Shh is a downstream target of Fgf10/Fgfr2b signaling. Our results demonstrate that mesenchymal Fgf10 regulates the epithelial expression of Shh, which in turn signals back to the mesenchyme. This was confirmed by demonstrating that cell proliferation is decreased not only in the palatal epithelium but also in the mesenchyme of Fgfr2b-/- mice. These results reveal a new role for Fgf signaling in mammalian palate development. We show that coordinated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions are essential during the initial stages of palate development and require an Fgf-Shh signaling network.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cleft palate: players, pathways, and pursuits.J Clin Invest. 2004 Jun;113(12):1676-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI22154. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15199400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gorlin, R.J., Cohen, M.M., Jr., and Hennekam, R.C.M. 2001. Syndromes of the head and neck. 4th edition. Oxford University Press. New York, New York, USA. 850–853.
-
- Jones MC. Etiology of facial clefts: prospective evaluation of 428 patients. Cleft Palate J. 1988;25:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Murray J. Gene/environment causes of cleft lip and/or palate. Clin. Genet. 2002;61:248–256. - PubMed
-
- Wilkie AO, Morriss-Kay GM. Genetics of craniofacial development and malformation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001;2:458–468. - PubMed
-
- Rice DP, et al. Integration of FGF and TWIST in calvarial bone and suture development. Development. 2000;127:1845–1855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

