Specific induction of neuronal cells from bone marrow stromal cells and application for autologous transplantation
- PMID: 15199405
- PMCID: PMC420509
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20935
Specific induction of neuronal cells from bone marrow stromal cells and application for autologous transplantation
Abstract
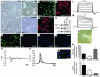
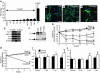
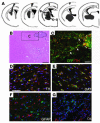
Bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs) have the capability under specific conditions of differentiating into various cell types such as osteocytes, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. Here we demonstrate a highly efficient and specific induction of cells with neuronal characteristics, without glial differentiation, from both rat and human MSCs using gene transfection with Notch intracellular domain (NICD) and subsequent treatment with bFGF, forskolin, and ciliary neurotrophic factor. MSCs expressed markers related to neural stem cells after transfection with NICD, and subsequent trophic factor administration induced neuronal cells. Some of them showed voltage-gated fast sodium and delayed rectifier potassium currents and action potentials compatible with characteristics of functional neurons. Further treatment of the induced neuronal cells with glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) increased the proportion of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive and dopamine-producing cells. Transplantation of these GDNF-treated cells showed improvement in apomorphine-induced rotational behavior and adjusting step and paw-reaching tests following intrastriatal implantation in a 6-hydroxy dopamine rat model of Parkinson disease. This study shows that a population of neuronal cells can be specifically generated from MSCs and that induced cells may allow for a neuroreconstructive approach.
Figures



References
-
- Kawasaki H, et al. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity. Neuron. 2000;28:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, Black IB. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000;61:364–370. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Ramos JR. Neural cells derived from adult bone marrow and umbilical cord blood. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002;69:880–893. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418:41–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

