Rubratoxin B elicits antioxidative and DNA repair responses in mouse brain
- PMID: 15200233
- PMCID: PMC5991149
- DOI: 10.3727/000000003783992261
Rubratoxin B elicits antioxidative and DNA repair responses in mouse brain
Abstract
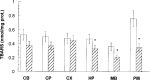
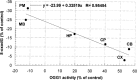
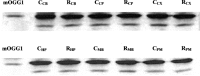
Rubratoxin B (RB) is a mycotoxin with potential neurotoxic effects that have not yet been characterized. Based on existing evidence that RB interferes with mitochondrial electron transport to produce oxidative stress in peripheral tissues, we hypothesized that RB would produce oxidative damage to macromolecules in specific brain regions. Parameters of oxidative DNA damage and repair, lipid peroxidation, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were measured across six mouse brain regions 24 h after administration of a single dose of RB. Lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage were either unchanged or decreased in all brain regions in RB-treated mice compared with vehicle-treated mice. Concomitant with these decreased indices of oxidative macromolecular damage, SOD activity was significantly increased in all brain regions. Oxyguanosine glycosylase activity (OGG1), a key enzyme in the repair of oxidized DNA, was significantly increased in three brain regions--cerebellum (CB), caudate/putamen (CP), and cortex (CX)--but not in the hippocampus (HP), midbrain (MB), and pons/medulla (PM). The RB-enhanced OGG1 catalytic activity in these brain regions was not due to increased OGG1 protein expression, but was a result of enhanced catalytic activity of the enzyme. In conclusion, specific brain regions responded to an acute dose of RB by significantly altering SOD and OGG1 activities to maintain the degree of oxidative DNA damage equal to, or less than, that of normal steady-state levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute neurotoxic effects of the fungal metabolite ochratoxin-A.Neurotoxicology. 2006 Jan;27(1):82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Neurotoxicology. 2006. PMID: 16140385
-
Neuroanatomical mapping of DNA repair and antioxidative responses in mouse brain: Effects of a single dose of MPTP.Neurotoxicology. 2006 Dec;27(6):1080-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2006.05.023. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Neurotoxicology. 2006. PMID: 16831462
-
Oxidative DNA damage in the aging mouse brain.Mov Disord. 1999 Nov;14(6):972-80. doi: 10.1002/1531-8257(199911)14:6<972::aid-mds1010>3.0.co;2-0. Mov Disord. 1999. PMID: 10584672
-
Dieldrin elicits a widespread DNA repair and antioxidative response in mouse brain.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2007;21(3):125-35. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20165. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17623884
-
DNA damage, repair, and antioxidant systems in brain regions: a correlative study.Free Radic Biol Med. 2000 Mar 1;28(5):779-85. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00172-6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000. PMID: 10754274
Cited by
-
Evaluation of In Vitro Pharmacological Activities and HRLC-MS Based Profiling of Phlogacanthus jenkinsii C. B. Clarke.J Pharmacopuncture. 2025 Jun 30;28(2):116-126. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2025.28.2.116. J Pharmacopuncture. 2025. PMID: 40589478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardozo-Pelaez F.; Stedeford T. J.; Brooks P. J.; Song S.; Sanchez-Ramos J. R. Effects of diethylmale-ate on DNA damage and repair in the mouse brain. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33:292–298; 2002. - PubMed
-
- Cascio C.; Guarneri R.; Russo D.; De Leo G.; Guarneri M.; Piccoli F.; Guarneri P. Pregnenolone sulfate, a naturally occurring excitotoxin involved in delayed retinal cell death. J. Neurochem. 74(6):2380–2391; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Dianov G.; Bischoff C.; Piotrowski J.; Bohr V. A. Repair pathways for processing of 8-oxoguanine in DNA by mammalian cell extracts. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 33811–33816; 1998. - PubMed
-
- Elstner E. F.; Heupel A. Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: A simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal. Biochem. 70:616–620; 1976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
