Tono-Pen XL calibration curves for cats, cows and sheep
- PMID: 15200622
- PMCID: PMC6746305
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2004.04038.x
Tono-Pen XL calibration curves for cats, cows and sheep
Abstract
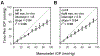
The objective of this study was to provide calibration curves for correcting intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements obtained using the Tono-Pen XL tonometer in cats, cows and sheep. Twelve eyes from 9 cats, 13 eyes from 7 cows, 10 eyes from 5 sheep were used. The anterior chamber of the eye was cannulated in vivo, in situ (immediately post mortem) or ex vivo with a fine needle and IOP was varied from 10 to 90 mmHg in steps of 10 mmHg by adjusting the height of a saline reservoir connected to the needle. For each pressure setting, several readings of IOP were made using the tonometer. The relationship between Tono-Pen reading and manometer setting was linear over the full range of measurement. However, the slope of the data regression line deviated significantly from 1 and indicated that the instrument systematically underestimated IOP. For cats the average slope was 0.62 and for cows and sheep it was 0.72 and 0.69, respectively. For the latter animals, the regression line also had a nonzero intercept of approximately 4.5 mmHg. Similar results were obtained from in vivo and ex vivo eyes and with different Tono-Pen XL tonometers. Although developed for use on humans, the Tono-Pen XL can provide reproducible and accurate measurement of IOP in cats, cows and sheep when suitably calibrated by manometry. The calibration curves provided here, and by implication those reported for other animals using this tonometer, differ in slope from those measured with earlier models of the Tono-Pen. The reproducibility of the curves we obtained implies that they can be used to correct IOP readings from the Tono-Pen XL when manometry is not possible.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of the TonoVet® rebound tonometer in normal and glaucomatous cats.Vet Ophthalmol. 2013 Mar;16(2):111-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2012.01038.x. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Vet Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 22672669 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intraocular pressure measurements between the Tono-Pen XL® and Perkins® applanation tonometers in dogs and cats.Vet Ophthalmol. 2012 Mar;15 Suppl 1:14-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2011.00926.x. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Vet Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22050624
-
Tonometer validation and intraocular pressure reference values in the normal chinchilla (Chinchilla lanigera).Vet Ophthalmol. 2018 Jan;21(1):4-9. doi: 10.1111/vop.12468. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Vet Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 28303681
-
Clinical comparison of the TonoVet(®) rebound tonometer and the Tono-Pen Vet(®) applanation tonometer in dogs and cats with ocular disease: glaucoma or corneal pathology.Vet Ophthalmol. 2015 Jan;18(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/vop.12101. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Vet Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 24131625
-
Agreement of tonometer for measuring intraocular pressure in Wistar rats: a systematic review.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 16;29(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01927-z. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38880889 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Management of bilateral uveitis in a Toxoplasma gondii-seropositive cat with histopathologic evidence of fungal panuveitis.Vet Ophthalmol. 2007 Jul-Aug;10(4):216-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2007.00541.x. Vet Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17565553 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of dorzolamide 2% on circadian intraocular pressure in cats with primary congenital glaucoma.Vet Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep;14 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):48-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2011.00913.x. Vet Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21923823 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of three methodologies for measuring intraocular pressure in healthy cats.Vet World. 2024 Aug;17(8):1803-1809. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.1803-1809. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39328448 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the TonoVet® rebound tonometer in normal and glaucomatous cats.Vet Ophthalmol. 2013 Mar;16(2):111-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2012.01038.x. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Vet Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 22672669 Free PMC article.
-
Control values of intraocular pressure in different species: a review of literature.Croat Med J. 2024 Dec 30;65(6):518-529. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2024.65.518. Croat Med J. 2024. PMID: 39812101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moore CG, Milne ST, Morrison JC. Noninvasive measurement of rat intraocular pressure with the Tono-Pen. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1993; 34: 363–369. - PubMed
-
- Mermoud A, Baerveldt G, Minckler DS, Lee MB, Rao NA. Measurement of rabbit intraocular pressure with the Tono-Pen. Ophthalmologica 1995; 209: 275–277. - PubMed
-
- Abrams LS, Vitale S, Jampel HD. Comparison of three tonometers for measuring intraocular pressure in rabbits. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1996; 37: 940–944. - PubMed
-
- Peterson JA, Kiland JA, Croft MA, Kaufman PL. Intraocular pressure measurement in cynomolgus monkeys. Tono-Pen versus manometry. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1996; 37: 1197–1199. - PubMed
-
- Miller PE, Pickett JP, Majors LJ, Kurzman ID. Evaluation of two applanation tonometers in cats. American Journal of Veterinary Research 1991; 52: 1917–1921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

