Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and serologic responses to Pneumocystis jiroveci
- PMID: 15200818
- PMCID: PMC3323219
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1005.030497
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and serologic responses to Pneumocystis jiroveci
Abstract
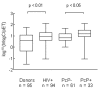
Seroepidemiologic studies of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in humans have been limited by inadequate reagents. We have developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using three overlapping recombinant fragments of the human Pneumocystis major surface glycoprotein (MsgA, MsgB, and MsgC) for analysis of antibody responses in HIV-positive patients and healthy blood donors. HIV-positive patients had significantly higher antibody levels to all Msg fragments. Furthermore, HIV-positive patients who experienced a previous episode of PCP (PCP-positive) had higher levels of antibodies to MsgC than patients who never had PCP. A significant association was found between ELISA antibody level and reactivity by Western blot in HIV-positive patients, especially those who were PCP-positive. Thus, this ELISA will be useful in studying serum antibody responses to Pneumocystis in different human populations.
Figures
References
-
- Meuwissen JH, Tauber I, Leeuwenberg AD, Beckers PJ, Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977;136:43–9. - PubMed
-
- Pifer LL, Hughes WT, Stagno S, Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978;61:35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
