Causative agent of Pogosta disease isolated from blood and skin lesions
- PMID: 15200824
- PMCID: PMC3323234
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1005.030689
Causative agent of Pogosta disease isolated from blood and skin lesions
Abstract
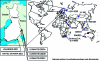
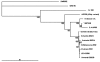
Pogosta disease is a mosquito-borne viral disease in Finland, which is clinically manifested by rash and arthritis; larger outbreaks occur in 7-year intervals. The causative agent of the disease has been suspected of being closely related to Sindbis virus (SINV). We isolated SINV from five patients with acute Pogosta disease during an outbreak in fall 2002 in Finland. One virus strain was recovered from a whole blood sample and four other strains from skin lesions. The etiology of Pogosta disease was confirmed by these first Finnish SINV strains, which also represent the first human SINV isolates from Europe. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the Finnish SINV strains are closely related to the viral agents that were previously isolated from mosquitoes and that are related clinically similar diseases in nearby geographic areas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection and isolation of Sindbis virus from mosquitoes captured during an outbreak in Sweden, 2013.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015 Feb;15(2):133-40. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2014.1717. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015. PMID: 25700044
-
Complete coding sequence and molecular epidemiological analysis of Sindbis virus isolates from mosquitoes and humans, Finland.J Gen Virol. 2012 Sep;93(Pt 9):1984-1990. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.042853-0. Epub 2012 May 30. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22647374
-
Sindbis virus polyarthritis outbreak signalled by virus prevalence in the mosquito vectors.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Aug 29;13(8):e0007702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007702. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31465453 Free PMC article.
-
[Sindbis-related (Pogosta) virus epidemics every seventh year--does the biblical cycle come true again?].Duodecim. 2002;118(14):1439-44. Duodecim. 2002. PMID: 12271600 Review. Finnish. No abstract available.
-
Sindbis virus as a human pathogen-epidemiology, clinical picture and pathogenesis.Rev Med Virol. 2016 Jul;26(4):221-41. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1876. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Rev Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 26990827 Review.
Cited by
-
Inkoo and Sindbis viruses in blood sucking insects, and a serological study for Inkoo virus in semi-domesticated Eurasian tundra reindeer in Norway.Virol J. 2022 Jun 3;19(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01815-0. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35659694 Free PMC article.
-
Alphaviruses Detected in Mosquitoes in the North-Eastern Regions of South Africa, 2014 to 2018.Viruses. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):414. doi: 10.3390/v15020414. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851627 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of evidence for the presence of mosquito-borne arboviruses in the upper Rhine Valley, Germany, in 1999 to 2000.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Sep;48(9):3457-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01156-10. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20592140 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gamma interferon-dependent, noncytolytic clearance of sindbis virus infection from neurons in vitro.J Virol. 2005 May;79(9):5374-85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.9.5374-5385.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15827152 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide CRISPR screens and their applications in infectious disease.Front Genome Ed. 2023 Sep 19;5:1243731. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2023.1243731. eCollection 2023. Front Genome Ed. 2023. PMID: 37794981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taylor RM, Hurlbut HS, Work TH, Kingsbury JR, Frothingham TE. Sindbis virus: a newly recognized arthropod-transmitted virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955;4:844–6. - PubMed
-
- Lvov DK, Vladimirtseva EA, Butenko AM, Karabatsos N, Trent DW, Calisher CH. Identity of Karelian fever and Ockelbo viruses determined by serum dilution-plaque reduction neutralization tests and oligonucleotide mapping. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988;39:607–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
