Effects of spironolactone on endothelial function, vascular angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and other prognostic markers in patients with mild heart failure already taking optimal treatment
- PMID: 15201246
- PMCID: PMC1768327
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.017368
Effects of spironolactone on endothelial function, vascular angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and other prognostic markers in patients with mild heart failure already taking optimal treatment
Abstract
Objectives: To examine whether the favourable effects on endothelial function, vascular angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity, cardiac remodelling, autonomic function, and QT intervals of spironolactone in combination with ACE inhibitor also occur in patients with New York Heart Association class I-II congestive heart failure (CHF) taking optimal treatment (including beta blockers).
Methods: Double blind, crossover study comparing 12.5-50 mg/24 hours spironolactone (three months) with placebo in 43 patients with class I-II CHF taking ACE inhibitors and beta blockers.
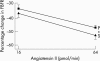
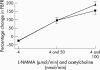
Results: Acetylcholine induced vasodilatation improved with spironolactone (p = 0.044). Vascular ACE activity fell (p = 0.006). QTc and QTd fell (mean (SD) QTc 473 (43.1) ms with placebo, 455 (35.4) ms with spironolactone, p = 0.002; QTd 84.5 (41.3) ms with placebo, 72.1 (32.3) ms with spironolactone, p = 0.037). beta-Type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and procollagen III N-terminal peptide (PIIINP) concentrations were also reduced by spironolactone (mean (SD) BNP 48.5 (29.6) pg/ml with placebo, 36.8 (28.5) pg/ml with spironolactone, p = 0.039; PIIINP 3.767 (1.157) microg/ml with placebo, 3.156 (1.123) microg/ml with spironolactone, p = 0.000).
Conclusions: Spironolactone improves vascular function (endothelial function, vascular ACE activity) and other markers of prognosis (BNP, collagen markers, and QT interval length) in asymptomatic or mild CHF when added to optimal treatment including beta blockade. This gives support to the hypothesis that the prognostic benefit seen in RALES (randomised aldactone evaluation study) and EPHESUS (eplerenone postacute myocardial infarction heart failure efficacy and survival study) may also occur in patients with milder CHF already taking standard optimal treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cost effectiveness of eplerenone in patients with heart failure after acute myocardial infarction who were taking both ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers: subanalysis of the EPHESUS.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10(1):55-63. doi: 10.2165/11319940-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20104935
-
Short-term improvement in submaximal exercise capacity by optimized therapy with ACE inhibitors and beta blockers in heart failure patients is associated with restoration of peripheral endothelial function.Int J Cardiol. 2006 Mar 22;108(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2005.04.003. Int J Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16516697
-
Efficacy and tolerability of adding an angiotensin receptor blocker in patients with heart failure already receiving an angiotensin-converting inhibitor plus aldosterone antagonist, with or without a beta blocker. Findings from the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM)-Added trial.Eur J Heart Fail. 2008 Feb;10(2):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.12.006. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008. PMID: 18242128 Clinical Trial.
-
Cardioprotection by aldosterone receptor antagonism in heart failure. Part I. The role of aldosterone in heart failure.Fiziol Cheloveka. 2005 Nov-Dec;31(6):97-105. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2005. PMID: 16366159 Review.
-
Aldosterone blockade over and above ACE-inhibitors in patients with coronary artery disease but without heart failure.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2006 Mar;7(1):20-30. doi: 10.3317/jraas.2006.002. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2006. PMID: 17083070 Review.
Cited by
-
The Prescription Characteristics, Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in Real-World Patients With Acute Heart Failure Syndrome: A Prospective Nationwide Cohort Study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 22;9:791446. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.791446. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35274010 Free PMC article.
-
The endothelial mineralocorticoid receptor: Contributions to sex differences in cardiovascular disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Nov;203:107387. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.06.009. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31271793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and endothelial function.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Sep;9(9):963-9. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18729003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional mineralocorticoid receptors in human vascular endothelial cells regulate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and promote leukocyte adhesion.Circ Res. 2008 Jun 6;102(11):1359-67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.174235. Epub 2008 May 8. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18467630 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to determine the effects of valsartan on exercise time in patients with symptomatic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2009 Oct;11(10):980-9. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfp120. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009. PMID: 19789402 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Pitt B , Zannad F, Remme WJ, et al. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized aldactone evaluation study investigators. N Engl J Med 1999;341:709–17. - PubMed
-
- Pitt B , Remme WJ, Zannad F, et al. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with LV dysfunction after MI. N Engl J Med 2003;384:1309–21. - PubMed
-
- Struthers AD. Effect of aldosterone on the vascular bed: introducing aldosterone induced vasculopathy. In Braunwald E, ed. Harrison’s advances in cardiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2003:12–7.
-
- Farquharson CA, Struthers AD. Spironolactone increases nitric oxide bioactivity, improves endothelial vasodilator dysfunction, and suppresses vascular angiotensin I/angiotensin II conversion in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2000;101:594–7. - PubMed
-
- Farquharson C , Struthers AD. Aldosterone induces acute endothelial dysfunction in vivo in man: evidence for an aldosterone induced vasculopathy. Clin Sci 2002;103:425–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
