The juvenile myoclonic epilepsy GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subunit mutation A322D produces asymmetrical, subunit position-dependent reduction of heterozygous receptor currents and alpha1 subunit protein expression
- PMID: 15201329
- PMCID: PMC6729321
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1301-04.2004
The juvenile myoclonic epilepsy GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subunit mutation A322D produces asymmetrical, subunit position-dependent reduction of heterozygous receptor currents and alpha1 subunit protein expression
Abstract
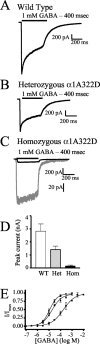
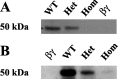
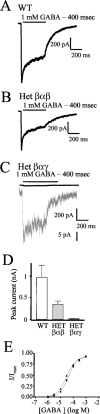
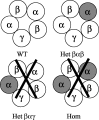
Individuals with autosomal dominant juvenile myoclonic epilepsy are heterozygous for a GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subunit mutation (alpha1A322D). GABA(A) receptor alphabetagamma subunits are arranged around the pore in a beta-alpha-beta-alpha-gamma sequence (counterclockwise from the synaptic cleft). Therefore, each alpha1 subunit has different adjacent subunits, and heterozygous expression of alpha1(A322D), beta, and gamma subunits could produce receptors with four different subunit arrangements: beta-alpha1-beta-alpha1-gamma (wild type); beta-alpha1(A322D)-beta-alpha1-gamma (Het(betaalphabeta)); beta-alpha1-beta-alpha1(A322D)-gamma (Het(betaalphagamma));beta-alpha1(A322D)-beta-alpha1(A322D)-gamma (homozygous). Expression of a 1:1 mixture of wild-type andalpha1(A322D) subunits with beta2S and gamma2S subunits (heterozygous transfection) produced smaller currents than wild type and much larger currents than homozygous mutant transfections. Western blot and biotinylation assays demonstrated that the amount of total and surface alpha1 subunit from heterozygous transfections was also intermediate between those of wild-type and homozygous mutant transfections. alpha1(A322D) mutations were then made in covalently tethered triplet (gamma2S-beta2S-alpha1) and tandem (beta2S-alpha1) concatamers to target selectively alpha1(A322D) to each of the asymmetric alpha1 subunits. Coexpression of mutant and wild-type concatamers resulted in expression of either Het(betaalphabeta) or Het(betaalphagamma) receptors. Het(betaalphabeta) currents were smaller than wild type and much larger than Het(betaalphagamma) and homozygous currents. Furthermore, Het(betaalphabeta) transfections contained less beta-alpha concatamer than wild type but more than both Het(betaalphagamma) and homozygous mutant transfections. Thus, whole-cell currents and protein expression of heterozygous alpha1(A322D)beta2Sgamma2S receptors depended on the position of the mutant alpha1 subunit, and GABA(A) receptor currents in heterozygous individuals likely result primarily from wild-type and Het(betaalphabeta) receptors with little contribution from Het(betaalphagamma) and homozygous receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The developmental evolution of the seizure phenotype and cortical inhibition in mouse models of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Oct;82:164-175. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26054439 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the A322D mutation in the GABA receptor alpha-subunit causing juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):10-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04168.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029191
-
GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subunit mutation A322D associated with autosomal dominant juvenile myoclonic epilepsy reduces the expression and alters the composition of wild type GABA(A) receptors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 20;285(34):26390-405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142299. Epub 2010 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20551311 Free PMC article.
-
gamma-Aminobutyric acid A receptor subunit mutant mice: new perspectives on alcohol actions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 15;68(8):1581-602. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.07.023. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15451402 Review.
-
Comparison of αβδ and αβγ GABAA receptors: Allosteric modulation and identification of subunit arrangement by site-selective general anesthetics.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Jul;133:289-300. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.12.031. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29294355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell genetic expression of mutant GABAA receptors causing Human genetic epilepsy alters dendritic spine and GABAergic bouton formation in a mutation-specific manner.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Oct 14;8:317. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00317. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352779 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Landscape of Common Epilepsies: Advancing towards Precision in Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 21;21(20):7784. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207784. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33096746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and Elevated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Epilepsy.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 11;10(3):647. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030647. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathology of genetic epilepsies associated with GABAA receptor subunit mutations.Epilepsy Curr. 2009 Jan-Feb;9(1):18-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2008.01278.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2009. PMID: 19396344 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of GABRG2 variants: a recurrent GABRG2 missense variant associated with a severe phenotype.J Neurogenet. 2017 Mar-Jun;31(1-2):30-36. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2017.1315417. Epub 2017 May 2. J Neurogenet. 2017. PMID: 28460589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Annegers JF, Rocca WA, Hauser WA (1996) Causes of epilepsy: contributions of the Rochester epidemiology project. Mayo Clin Proc 71: 570-575. - PubMed
-
- Barnes Jr EM (2000) Intracellular trafficking of GABA(A) receptors. Life Sci 66: 1063-1070. - PubMed
-
- Baumann SW, Baur R, Sigel E (2001) Subunit arrangement of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. J Biol Chem 276: 36275-36280. - PubMed
-
- Baumann SW, Baur R, Sigel E (2002) Forced subunit assembly in alpha 1beta 2gamma 2 GABAA receptors. Insight into the absolute arrangement. J Biol Chem 277: 46020-46025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
