Cone photoreceptors in bass retina use two connexins to mediate electrical coupling
- PMID: 15201336
- PMCID: PMC2222551
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1248-04.2004
Cone photoreceptors in bass retina use two connexins to mediate electrical coupling
Abstract
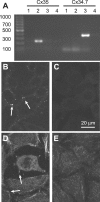
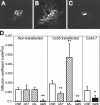
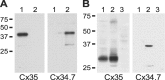
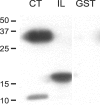
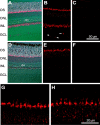
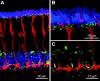
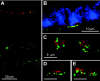
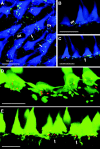
Electrical coupling via gap junctions is a common property of CNS neurons. In retinal photoreceptors, coupling plays important roles in noise filtering, intensity coding, and spatial processing. In many vertebrates, coupling is regulated during the course of light adaptation. To understand the mechanisms of this regulation, we studied photoreceptor gap junction proteins. We found that two connexins were expressed in bass cone photoreceptors. Connexin 35 (Cx35) mRNA was present in many cell types, including photoreceptors and amacrine, bipolar, and a few ganglion cells. Antibodies to Cx35 labeled abundant gap junctions in both the inner and outer plexiform layers. In the outer plexiform layer, numerous plaques colocalized with cone telodendria at crossing contacts and tip-to-tip contacts. Cx34.7 mRNA was found predominantly in the photoreceptor layer, primarily in cones. Cx34.7 immunolabeling was limited to small plaques immediately beneath cone pedicles and did not colocalize with Cx35. Cx34.7 plaques were associated with a dense complex of cone membrane beneath the pedicles, including apparent contacts between telodendria and cone pedicles. Tracer coupling studies of the connexins expressed in HeLa cells showed that coupling through Cx35 gap junctions was reduced by protein kinase A (PKA) activation and enhanced by PKA inhibition through a greater than fivefold activity range. Cx34.7 was too poorly expressed to study. PKA regulation suggests that coupling through Cx35 gap junctions can be controlled dynamically through dopamine receptor pathways during light adaptation. If Cx34.7 forms functional cell-cell channels between cones, it would provide a physically separate pathway for electrical coupling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning and expression of two related connexins from the perch retina define a distinct subgroup of the connexin family.J Neurosci. 1998 Oct 1;18(19):7625-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-07625.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9742134 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor coupling is controlled by connexin 35 phosphorylation in zebrafish retina.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 2;29(48):15178-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3517-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19955370 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine and dopamine receptors coregulate photoreceptor coupling via gap junction phosphorylation in mouse retina.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 13;33(7):3135-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2807-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23407968 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical synapses between AII amacrine cells in the retina: Function and modulation.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:160-72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.05.060. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22776293 Review.
-
Gap junctional coupling in the vertebrate retina: variations on one theme?Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 May;34:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23313713 Review.
Cited by
-
Mixed Electrical-Chemical Synapses in Adult Rat Hippocampus are Primarily Glutamatergic and Coupled by Connexin-36.Front Neuroanat. 2012 May 15;6:13. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2012.00013. eCollection 2012. Front Neuroanat. 2012. PMID: 22615687 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin composition in apposed gap junction hemiplaques revealed by matched double-replica freeze-fracture replica immunogold labeling.J Membr Biol. 2012 Jun;245(5-6):333-44. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9454-2. Epub 2012 Jul 4. J Membr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22760604 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junction Delta-2b (gjd2b/Cx35.1) depletion causes hyperopia and visual-motor deficiencies in the zebrafish.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 2;11:1150273. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1150273. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36936688 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-dependent binding of calmodulin to neuronal gap junction proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Oct 7;335(4):1191-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.007. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16112650 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fluorescent tracer for visualizing coupled cells in neural circuits of living tissue.J Histochem Cytochem. 2006 Oct;54(10):1169-76. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A6935.2006. Epub 2006 Jul 24. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006. PMID: 16864895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attwell D, Borges S, Wu SM, Wilson M (1987) Signal clipping by the rod output synapse. Nature 328: 522-524. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA, Xin D, Osborne T (1997) Light-induced modulation of coupling between AII amacrine cells in the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci 14: 565-576. - PubMed
-
- Condorelli DF, Parenti R, Spinella F, Salinaro AT, Belluardo N, Cardile V, Cicirata F (1998) Cloning of a new gap junction gene (Cx36) highly expressed in mammalian brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci 10: 1202-1208. - PubMed
-
- Cooper NG, McLaughlin BJ (1981) Gap junctions in the outer plexiform layer of the chick retina: thin section and freeze-fracture studies. J Neurocytol 10: 515-529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
