Nck-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and regulation of cell survival during endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 15201339
- PMCID: PMC515356
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0851
Nck-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and regulation of cell survival during endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
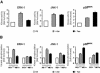
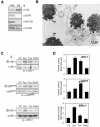
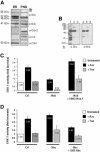
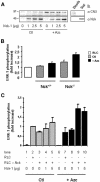
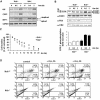
In response to stress, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) signaling machinery triggers the inhibition of protein synthesis and up-regulation of genes whose products are involved in protein folding, cell cycle exit, and/or apoptosis. We demonstrate that the misfolding agents azetidine-2-carboxylic acid (Azc) and tunicamycin initiate signaling from the ER, resulting in the activation of Jun-N-terminal kinase, p44(MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 (ERK-1), and p38(MAPK) through IRE1alpha-dependent mechanisms. To characterize the ER proximal signaling events involved, immuno-isolated ER membranes from rat fibroblasts treated with ER stress inducers were used to reconstitute the activation of the stress-activated protein kinase/mitogen-activate protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in vitro. This allowed us to demonstrate a role for the SH2/SH3 domain containing adaptor Nck in ERK-1 activation after Azc treatment. We also show both in vitro and in vivo that under basal conditions ER-associated Nck represses ERK-1 activation and that upon ER stress this pool of Nck dissociates from the ER membrane to allow ERK-1 activation. Moreover, under the same conditions, Nck-null cells elicit a stronger ERK-1 activation in response to Azc stress, thus, correlating with an enhanced survival phenotype. These data delineate a novel mechanism for the regulation of ER stress signaling to the MAPK pathway and demonstrate a critical role for Nck in ER stress and cell survival.
Figures



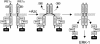
Similar articles
-
Nck in a complex containing the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 regulates eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha signaling and cell survival to endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26633-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513556200. Epub 2006 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16835242
-
Critical role of endogenous Akt/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 19;279(47):49420-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407700200. Epub 2004 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15339911
-
Nck-2, a novel Src homology2/3-containing adaptor protein that interacts with the LIM-only protein PINCH and components of growth factor receptor kinase-signaling pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Dec;9(12):3367-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.12.3367. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9843575 Free PMC article.
-
Protection of renal epithelial cells against oxidative injury by endoplasmic reticulum stress preconditioning is mediated by ERK1/2 activation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 1;278(31):29317-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302368200. Epub 2003 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12738790
-
[A uNick protein].Med Sci (Paris). 2011 Aug-Sep;27(8-9):746-52. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2011278017. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Med Sci (Paris). 2011. PMID: 21880263 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Calnexin phosphorylation attenuates the release of partially misfolded alpha1-antitrypsin to the secretory pathway.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 11;284(50):34570-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.053165. Epub 2009 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19815548 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Sensor IRE1α in Cellular Physiology, Calcium, ROS Signaling, and Metaflammation.Cells. 2020 May 8;9(5):1160. doi: 10.3390/cells9051160. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32397116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A molecular web: endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Jul 29;8:213. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00213. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25120434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nck2, an unexpected regulator of adipogenesis.Adipocyte. 2017 Apr 3;6(2):154-160. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2017.1291102. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Adipocyte. 2017. PMID: 28425845 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces hepatic plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.FASEB Bioadv. 2020 Oct 10;2(12):695-704. doi: 10.1096/fba.2020-00056. eCollection 2020 Dec. FASEB Bioadv. 2020. PMID: 33336157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aridor, M., and Balch, W.E. (1999). Integration of endoplasmic reticulum signaling in health and disease. Nat. Med. 5, 745–751. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa-Tessmann, I.P., Chen, C., Zhong, C., Schuster, S.M., Nick, H.S., and Kilberg, M.S. (1999). Activation of the unfolded protein response pathway induces human asparagine synthetase gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31139–31144. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A.W., et al. (2001). Proteomics characterization of abundant Golgi membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 5152–5165. - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti, A., Zhang, Y., Hendershot, L.M., Harding, H.P., and Ron, D. (2000). Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 326–332. - PubMed
-
- Bork, P., and Sander, C. (1993). A hybrid protein kinase-RNase in an interferon-induced pathway? FEBS Lett. 334, 149–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

