Links between CD147 function, glycosylation, and caveolin-1
- PMID: 15201341
- PMCID: PMC515339
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0402
Links between CD147 function, glycosylation, and caveolin-1
Abstract
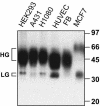
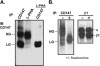
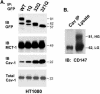
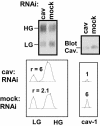
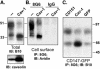
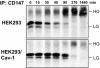
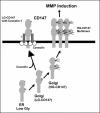
Cell surface CD147 shows remarkable variations in size (31-65 kDa) because of heterogeneous N-glycosylation, with the most highly glycosylated forms functioning to induce matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production. Here we show that all three CD147 N-glycosylation sites make similar contributions to both high and low glycoforms (HG- and LG-CD147). l-Phytohemagglutinin lectin binding and swainsonine inhibition experiments indicated that HG-CD147 contains N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V-catalyzed, beta1,6-branched, polylactosamine-type sugars, which account for its excess size. Therefore, CD147, which is itself elevated on invasive tumor cells, may make a major contribution to the abundance of beta1,6-branched polylactosamine sugars that appear on invasive tumor cells. It was shown previously that caveolin-1 associates with CD147, thus inhibiting CD147 self-aggregation and MMP induction; now we show that caveolin-1 associates with LG-CD147 and restricts the biosynthetic conversion of LG-CD147 to HG-CD147. In addition, HG-CD147 (but not LG-CD147) was preferentially captured as a multimer after treatment of cells with a homobifunctional cross-linking agent and was exclusively recognized by monoclonal antibody AAA6, a reagent that selectively recognizes self-associated CD147 and inhibits CD147-mediated MMP induction. In conclusion, we have 1) determined the biochemical basis for the unusual size variation in CD147, 2) established that CD147 is a major carrier of beta1,6-branched polylactosamine sugars on tumor cells, and 3) determined that caveolin-1 can inhibit the conversion of LG-CD147 to HG-CD147. Because it is HG-CD147 that self-aggregates and stimulates MMP induction, we now have a mechanism to explain how caveolin-1 inhibits these processes. These results help explain the previously established tumor suppressor functions of caveolin-1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 15;15(4):6356-77. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046356. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24739808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 regulates matrix metalloproteinases-1 induction and CD147/EMMPRIN cell surface clustering.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 19;279(12):11112-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312947200. Epub 2004 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14707126
-
β3GnT8 plays an important role in CD147 signal transduction as an upstream modulator of MMP production in tumor cells.Oncol Rep. 2014 Sep;32(3):1156-62. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3280. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24970053
-
Caveolin-1 up-regulates CD147 glycosylation and the invasive capability of murine hepatocarcinoma cell lines.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(9):1584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.03.019. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16702020
-
EMMPRIN/CD147, an MMP modulator in cancer, development and tissue repair.Biochimie. 2005 Mar-Apr;87(3-4):361-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.09.023. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15781323 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the complex interactions between Rab22a and extracellular vesicles in cancers.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jan;73(1):99-110. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01821-0. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38066108 Review.
-
Modification of sialylation is associated with multidrug resistance in human acute myeloid leukemia.Oncogene. 2015 Feb 5;34(6):726-40. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.7. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24531716
-
Clinical impact of HAb18G/CD147 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Dec;56(12):3569-76. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1812-x. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21789540
-
Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 8;19(2):507. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020507. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29419744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 15;15(4):6356-77. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046356. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24739808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aldred, M.A., et al. (2003). Caveolin-1 and caveolin-2, together with three bone morphogenetic protein-related genes, may encode novel tumor suppressors down-regulated in sporadic follicular thyroid carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 63, 2864-2871. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., Chang, S., Bodorova, J., and Hemler, M.E. (1997). Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin-associated proteins: evidence that α3β1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29174-29180. - PubMed
-
- Biswas, C., Zhang, Y., DeCastro, R., Guo, H., Nakamura, T., Kataoka, H., and Nabeshima, K. (1995). The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res. 55, 434-439. - PubMed
-
- Bordador, L.C., Li, X., Toole, B., Chen, B., Regezi, J., Zardi, L., Hu, Y., and Ramos, D.M. (2000). Expression of emmprin by oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 85, 347-352. - PubMed
-
- Caudroy, S., Polette, M., Nawrocki-Raby, B., Cao, J., Toole, B.P., Zucker, S., and Birembaut, P. (2002). EMMPRIN-mediated MMP regulation in tumor and endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 19, 697-702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

