Mdc1 couples DNA double-strand break recognition by Nbs1 with its H2AX-dependent chromatin retention
- PMID: 15201865
- PMCID: PMC449779
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600269
Mdc1 couples DNA double-strand break recognition by Nbs1 with its H2AX-dependent chromatin retention
Abstract
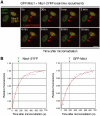
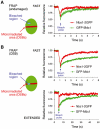
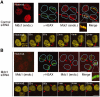
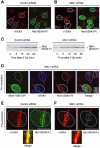
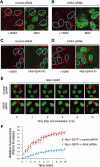
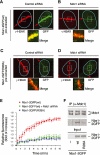
Mdc1/NFBD1 controls cellular responses to DNA damage, in part via interacting with the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex that is involved in the recognition, signalling, and repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Here, we show that in live human cells, the transient interaction of Nbs1 with DSBs and its phosphorylation by ATM are Mdc1-independent. However, ablation of Mdc1 by siRNA or mutation of the Nbs1's FHA domain required for Mdc1 binding reduced the affinity of Nbs1 for DSB-flanking chromatin and caused aberrant pan-nuclear dispersal of Nbs1. This occurred despite normal phosphorylation of H2AX, indicating that lack of Mdc1 does not impair this DSB-induced chromatin change, but rather precludes the sustained engagement of Nbs1 with these regions. Mdc1 (but not Nbs1) became partially immobilized to chromatin after DSB generation, and siRNA-mediated depletion of H2AX prevented such relocalization of Mdc1 and uncoupled Nbs1 from DSB-flanking chromatin. Our data suggest that Mdc1 functions as an H2AX-dependent interaction platform enabling a switch from transient, Mdc1-independent recruitment of Nbs1 to DSBs towards sustained, Mdc1-dependent interactions with the surrounding chromosomal microenvironment.
Figures
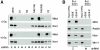
References
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421: 499–506 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296: 550–553 - PubMed
-
- Celeste A, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Kruhlak MJ, Pilch DR, Staudt DW, Lee A, Bonner RF, Bonner WM, Nussenzweig A (2003) Histone H2AX phosphorylation is dispensable for the initial recognition of DNA breaks. Nat Cell Biol 5: 675–679 - PubMed
-
- Cerosaletti KM, Concannon P (2003) Nibrin forkhead-associated domain and breast cancer C-terminal domain are both required for nuclear focus formation and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 278: 21944–21951 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

