Plasma membrane microdomains: organization, function and trafficking
- PMID: 15204627
- PMCID: PMC3376445
- DOI: 10.1080/09687680410001700517
Plasma membrane microdomains: organization, function and trafficking
Abstract
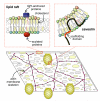
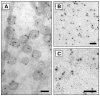
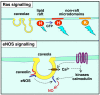
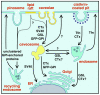
The plasma membrane consists of a mosaic of functional microdomains facilitating a variety of physiological processes associated with the cell surface. In most cells, the majority of the cell surface is morphologically featureless, leading to difficulties in characterizing its organization and microdomain composition. The reliance on indirect and perturbing techniques has led to vigorous debate concerning the nature and even existence of some microdomains. Recently, increasing technical sophistication has been applied to study cell surface compartmentalization providing evidence for small, short-lived clusters that may be much less than 50 nm in diameter. Lipid rafts and caveolae are cholesterol-dependent, highly ordered microdomains that have received most attention in recent years, yet their precise roles in regulating functions such as cell signalling remain to be determined. Endocytosis of lipid rafts/caveolae follows a clathrin-independent route to both early endosomes and non-classical caveosomes. The observation that a variety of cellular pathogens localize to and internalize with these microdomains provides an additional incentive to characterize the organization, dynamics and functions of these domains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endocytosis without clathrin coats.Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;11(10):406-12. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02107-9. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11567873 Review.
-
Lipid rafts and plasma membrane microorganization: insights from Ras.Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;14(3):141-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.02.001. Trends Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15003623 Review.
-
Roles of lipid rafts in membrane transport.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;13(4):470-7. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00238-6. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11454454 Review.
-
Direct visualization of Ras proteins in spatially distinct cell surface microdomains.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jan 20;160(2):165-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200209091. Epub 2003 Jan 13. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12527752 Free PMC article.
-
Caveosomes and endocytosis of lipid rafts.J Cell Sci. 2003 Dec 1;116(Pt 23):4707-14. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00840. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 14600257 Review.
Cited by
-
Unremodeled GPI-anchored proteins at the plasma membrane trigger aberrant endocytosis.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Nov 22;8(2):e202402941. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402941. Print 2025 Feb. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39578075 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Biomembrane Functions in Plant Responses to High-Temperature Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jul 3;9:915. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00915. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30018629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing a Dual Role of Ganglioside Lipids in the Aggregation of Membrane-Associated Islet Amyloid Polypeptide.J Membr Biol. 2019 Oct;252(4-5):343-356. doi: 10.1007/s00232-019-00074-5. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Membr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31222470
-
Ras hyperactivation versus overexpression: Lessons from Ras dynamics in Candida albicans.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 27;8(1):5248. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23187-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29588468 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of hepatitis C virus infection is dependent on cholesterol and cooperativity between CD81 and scavenger receptor B type I.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):374-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01134-06. Epub 2006 Oct 18. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17050612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SN, Brown DA, London E. On the origin of sphingolipid-cholesterol rich detergent-insoluble domains in cell membranes: physiological concentrations of cholesterol and sphingolipid induce formation of a detergent-insoluble, liquid-ordered lipid phase in model membranes. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10944–10953. - PubMed
-
- Baron W, Decker L, Colognato H, ffrench-Constant C. Regulation of integrin growth factor interactions in oligodendrocytes by lipid raft microdomains. Current Biology. 2003;13:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, London E. Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 1998;14:111–136. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Rose JK. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipids-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992;68:533–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
