Pharmacokinetics of S-3-(4-acetylamino-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-nitro- 3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-propionamide in rats, a non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator
- PMID: 15204699
- PMCID: PMC2040234
- DOI: 10.1080/0049825041008962
Pharmacokinetics of S-3-(4-acetylamino-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-nitro- 3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-propionamide in rats, a non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator
Abstract
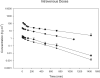
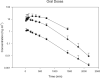
1: S-3-(4-acetylamino-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-nitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-propionamide (also known as S-4) is a non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator demonstrating tissue-selective androgenic and anabolic effects. The purpose of the present study was to examine the systemic pharmacokinetics, elimination and oral bioavailability of S-4 in rats. 2: Thirty-five male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing approximately 250 g were randomly assigned to one of seven treatment groups. Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1, 10, and 30 mg kg(-1) were given via a jugular catheter. Oral doses of 1, 10 and 30 mg kg(-1) were administered via gavage. Plasma concentrations were determined using a validated high-performance liquid chromatography or by a high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry method. 3: Clearances ranged between 1.0 and 2.1 ml min(-1) kg(-1) and varied with dose. The volume of distribution was approximately 0.448 l kg(-1) in all treatment groups. Oral bioavailability was also dose dependent, with the lower doses showing complete oral bioavailability. The half-life of S-4 over the dose range tested was between 2.6 and 5.3 h. 4: It was demonstrated that S-4 is rapidly absorbed, slowly cleared, and has a moderate volume of distribution in rats. The pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of S-4 indicate that it is an excellent candidate for clinical development.
Copyright 2004 Taylor and Francis Ltd.
Figures
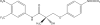
Similar articles
-
Interspecies differences in pharmacokinetics and metabolism of S-3-(4-acetylamino-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-nitro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-propionamide: the role of N-acetyltransferase.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Feb;34(2):254-60. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007120. Epub 2005 Nov 4. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16272403 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of a selective androgen receptor modulator in rats: implication of molecular properties and intensive metabolic profile to investigate ideal pharmacokinetic characteristics of a propanamide in preclinical study.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Mar;34(3):483-94. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.006643. Epub 2005 Dec 28. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16381665 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo metabolism and final disposition of a novel nonsteroidal androgen in rats and dogs.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Oct;34(10):1713-21. doi: 10.1124/dmd.106.009985. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16815963
-
Selective androgen receptor modulator treatment improves muscle strength and body composition and prevents bone loss in orchidectomized rats.Endocrinology. 2005 Nov;146(11):4887-97. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0572. Epub 2005 Aug 11. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 16099859 Free PMC article.
-
A selective androgen receptor modulator for hormonal male contraception.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Feb;312(2):546-53. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.075424. Epub 2004 Sep 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15347734
Cited by
-
Selective androgen receptor modulators in preclinical and clinical development.Nucl Recept Signal. 2008;6:e010. doi: 10.1621/nrs.06010. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Nucl Recept Signal. 2008. PMID: 19079612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interspecies differences in pharmacokinetics and metabolism of S-3-(4-acetylamino-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(4-nitro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-propionamide: the role of N-acetyltransferase.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Feb;34(2):254-60. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007120. Epub 2005 Nov 4. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16272403 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of a selective androgen receptor modulator in rats: implication of molecular properties and intensive metabolic profile to investigate ideal pharmacokinetic characteristics of a propanamide in preclinical study.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Mar;34(3):483-94. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.006643. Epub 2005 Dec 28. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16381665 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nonsteroidal androgen receptor ligands.Pharm Res. 2006 Aug;23(8):1641-58. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-9024-3. Pharm Res. 2006. PMID: 16841196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The androgen receptor and its use in biological assays: looking toward effect-based testing and its applications.J Anal Toxicol. 2011 Nov;35(9):594-607. doi: 10.1093/anatox/35.9.594. J Anal Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 22080898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhasin S, Bremner WJ. Clinical review 85: Emerging issues in androgen replacement therapy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1997;82:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Boyle GW, McKillop D, Phillips PJ, Harding JR, Pickford R, McCormick AD. Metabolism of casodex in laboratory animals. Xenobiotica. 1993;23:781–798. - PubMed
-
- Dalton JT, Mukherjee A, Zhu Z, Kirkovsky L, Miller DD. Discovery of nonsteroidal androgens. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1998;244:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Davies B, Morris T. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharmaceutical Research. 1993;10:1093–1095. - PubMed
-
- Handelsman DJ, Conway AJ, Boylan LM. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of testosterone pellets in man. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1990;71:216–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
