Characterization and evolution of diffusion MR imaging abnormalities in stroke patients undergoing intra-arterial thrombolysis
- PMID: 15205129
- PMCID: PMC7975652
Characterization and evolution of diffusion MR imaging abnormalities in stroke patients undergoing intra-arterial thrombolysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Lesions revealed by pretreatment diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) may not progress to infarction, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) or DWI thresholds for tissue viability may exist. We evaluated the evolution of abnormal DWI findings in patients with acute stroke who underwent thrombolysis.
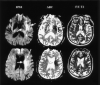
Methods: Sixteen patients with acute occlusion of the anterior circulation underwent DWI followed by intra-arterial thrombolysis; follow-up CT or MR imaging was performed after reperfusion therapy. Lesion volumes were measured on all images. In three patients with abnormal DWI findings that appeared normal at follow-up, ADC values, ADC ratios, and DWI ratios were obtained on a section-by-section basis in the DWI-hyperintense regions that were either abnormal or normal at follow-up.
Results: In three patients, part of the DWI-hyperintense tissue appeared normal and part appeared abnormal at follow-up imaging. In one of these patients, the lesion decreased by -35.6%. In the other two, lesion growth appeared in regions that appeared normal at initial DWI: in one, the overall change in size was -2.4%, and in the other, the lesion increased by 89.8%. Respective mean changes at follow-up in normal-appearing and abnormal-appearing regions were: ADC, 731.7 x 10(-6) mm(2)/s and 650.4 x 10(-6) mm (2)/s; ADC ratio, 0.92 and 0.78; and DWI ratio, 1.16 and 1.32 (P <.001 for all measures).
Conclusion: In patients with acute stroke who undergo intra-arterial thrombolysis, most abnormal, pretreatment DWI findings indicate eventual infarction. In 19% of the patients described herein, DWI-hyperintense regions appeared normal at follow-up. ADC values, ADC ratios, and DWI ratios may be useful in identifying the portion of abnormal tissue that is potentially salvageable after reperfusion therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Furlan A, Higashida R, Weschler L, et al. Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial—Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism. JAMA 1999;282:2003–2011 - PubMed
-
- Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581–1587 - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez RG, Schaefer PW, Buonanno, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging: diagnostic accuracy in patients imaged within 6 hours of stroke symptom onset. Radiology 1999;210:155–162 - PubMed
-
- Marks MP, De Crespigny A, Lentz D, Enzmann DR, Albers GW, Moseley ME. Acute and chronic stroke: navigated spin-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 1996;199:403–408 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
