MMP inhibition prevents human lens epithelial cell migration and contraction of the lens capsule
- PMID: 15205227
- PMCID: PMC1772237
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2003.034629
MMP inhibition prevents human lens epithelial cell migration and contraction of the lens capsule
Abstract
Purpose: The development of posterior capsule contraction following cataract surgery is caused by the activity of residual lens epithelial cells. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a group of proteolytic enzymes, which are essential for cell migration and cell mediated contraction following wound healing. The authors investigated whether inhibiting MMP activity can reduce lens epithelial cell migration and as a result, lead to a reduction in cell mediated capsule contraction.
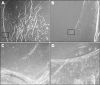
Methods: Human donor lens capsules were cultured and treated with a broad spectrum MMP inhibitor, Ilomastat (GM6001). MMP-2 and MMP-9 production were determined by ELISA. Cell migration onto the posterior capsule and capsule contraction were digitally measured.
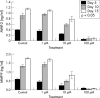
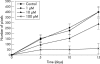
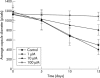
Results: MMP inhibition significantly reduced lens epithelial cell migration onto the posterior capsule (p<0.05), and a reduction in capsule contraction was observed (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Ilomastat significantly reduced lens epithelial cell migration onto the posterior capsule surface and inhibited capsule contraction. MMP inhibition may have a role in the therapeutic treatment of posterior capsule opacification.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Study on inhibitory effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor on migration of cultured human lens epithelial cells].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Apr;44(4):315-20. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18844017 Chinese.
-
Type I collagen accelerates the spreading of lens epithelial cells through the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinases.Curr Eye Res. 2014 May;39(5):460-71. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2013.853194. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Curr Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24400880
-
MMP2 activity is critical for TGFβ2-induced matrix contraction--implications for fibrosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Jun 26;53(7):4085-98. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9457. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22618590
-
[Pathogenesis of posterior capsule opacification in pseudophakia].Klin Oczna. 2009;111(10-12):369-74. Klin Oczna. 2009. PMID: 20169899 Review. Polish.
-
Posterior capsule opacification.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006 Feb;17(1):45-53. doi: 10.1097/01.icu.0000193074.24746.e6. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16436924 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of delivery of MMP inhibitors from PDMS as a model IOL material on PCO markers.Biomaterials. 2010 Mar;31(8):2399-407. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.11.108. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20022368 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases as Mediators of Primary and Secondary Cataracts.Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2007;2(6):931-938. doi: 10.1586/17469899.2.6.931. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 19018298 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 activities in the human lens epithelial cells and serum of steroid induced posterior subcapsular cataracts.Mol Vis. 2012;18:64-73. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22259225 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of MMP-2 and -9 by proteasome inhibition: a possible mechanism to decrease LEC migration and prevent posterior capsular opacification.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 May;49(5):1998-2003. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0624. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18436832 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of MMP inhibitor GM6001 on early fibroblast-mediated collagen matrix contraction is correlated to a decrease in cell protrusive activity.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;90(1):26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.09.008. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21040999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishi O , Nishi K, Wickstrom K. Preventing lens epithelial cell migration using intraocular lenses with sharp rectangular edges. J Cataract Refract Surg 2000;26:1543–9. - PubMed
-
- Nishi O , Nishi K, Akura J, et al. Effect of round-edged acrylic intraocular lenses on preventing posterior capsule opacification. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001;27:608–13. - PubMed
-
- Apple DJ, Solomon KD, Tetz MR, et al. Posterior capsule opacification. Surv Ophthalmol 1992;37:73–116. - PubMed
-
- Kappelhof JP, Vrensen GF. The pathology of after-cataract. A minireview. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl 1992;205:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Apple DJ, Peng Q, Visessook N, et al. Eradication of PCO: documentation of a marked reduction in Nd:YAG laser posterior capsulotomy rates in an analysis of 5416 pseudophakic human eyes obtained postmortem. Ophthalmology 2001;108:505–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
