Attenuation by a sigma1 (sigma1) receptor agonist of the learning and memory deficits induced by a prenatal restraint stress in juvenile rats
- PMID: 15205309
- PMCID: PMC1575047
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705835
Attenuation by a sigma1 (sigma1) receptor agonist of the learning and memory deficits induced by a prenatal restraint stress in juvenile rats
Abstract
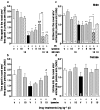
1. Stress during pregnancy results in complex neurochemical and behavioral alterations throughout the offspring lifetime. We here examined the impact of prenatal stress (PS) on memory functions in male and female offspring and report the efficacy of a selective sigma(1) (sigma(1)) receptor agonist, igmesine, in alleviating the observed deficits. 2. Dams received an unpredictable 90-min duration restraint stress from gestational day E17 to E20. Learning was examined in offspring between day P24 and P36 using spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze, delayed alternation in the T-maze, water-maze learning and passive avoidance. 3. Both male and female PS rats showed impairments of spontaneous and delayed alternation performances. Acquisition of a fixed platform position in the water-maze was unchanged in PS rats, but the probe test revealed a diminution of time spent in the training quadrant. Acquisition of a daily changing platform position demonstrated impaired working memory for male and female PS rats. Finally, passive avoidance deficits were observed. 4. Pretreatment with the selective sigma(1) agonist igmesine (1-10 mg x kg(-1) i.p.) reversed the PS-induced learning deficits in offspring rats for each test. The sigma(1) antagonist BD1063 failed to affect performances alone but blocked the igmesine effect, confirming the involvement of the sigma(1) receptor. 5. PS thus induces delayed memory deficits, affecting spatial and nonspatial, short- and long-term memories in juvenile male and female offspring rats. Activation of the sigma(1) neuromodulatory receptor allows a significant recovery of the memory functions in PS rats.
Figures




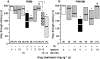
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effects of the sigma1 receptor agonists igmesine and dehydroepiandrosterone against learning impairments in rats prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2004 Nov-Dec;26(6):783-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2004.07.003. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2004. PMID: 15451042
-
Sex differences in learning deficits induced by prenatal stress in juvenile rats.Behav Brain Res. 2004 Apr 2;150(1-2):149-57. doi: 10.1016/S0166-4328(03)00250-X. Behav Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15033288
-
Concurrent exposure to aluminum and stress during pregnancy in rats: Effects on postnatal development and behavior of the offspring.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2005 Jul-Aug;27(4):565-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2005.06.014. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2005. PMID: 16024221
-
A meta-analysis of animal studies on disruption of spatial navigation by prenatal cocaine exposure.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007 Sep-Oct;29(5):570-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2007.06.003. Epub 2007 Jun 30. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007. PMID: 17683902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of σ1 Receptors in Learning and Memory and Alzheimer's Disease-Type Dementia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:213-233. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315274 Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's disease related markers, cellular toxicity and behavioral deficits induced six weeks after oligomeric amyloid-β peptide injection in rats.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053117. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23301030 Free PMC article.
-
Time-course and regional analyses of the physiopathological changes induced after cerebral injection of an amyloid β fragment in rats.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jul;179(1):315-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.021. Epub 2011 May 10. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21703413 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the sigma-1 receptor as a biological target to treat affective and cognitive disorders.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:1114-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.10.037. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34736882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder. A Translational Review in Animal Models of the Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016 Feb 17;9(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ph9010009. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26901205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Sigma-1 receptor chaperone's cellular functions: a microarray report.Synapse. 2012 Jan;66(1):42-51. doi: 10.1002/syn.20984. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Synapse. 2012. PMID: 21905129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALONSO G., PHAN V.L., GUILLEMAIN I., SAUNIER M., LEGRAND A., ANOAL M., MAURICE T. Immunocytochemical localization of the sigma1 (σ1) receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 2000;97:155–170. - PubMed
-
- BERGER M.A., BARROS V.G., SARCHI M.I., TARAZI F.I., ANTONELLI M.C. Long-term effects of prenatal stress on dopamine and glutamate receptors in adult rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 2002;27:1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- DE COSTA B.R., RADESCA L., DI PAOLO L., BOWEN W.D. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of a novel class of N-(arylethyl)-N-alkyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylamines: structural requirements and binding affinity at the sigma receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:38–47. - PubMed
-
- DEROCQ J.M., BOURRIE B., SEGUI M., LE FUR G., CASELLAS P. In vivo inhibition of endotoxin-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines production by the sigma ligand SR 31747. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995;272:224–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

