Regulation of the Ysa type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica by YsaE/SycB and YsrS/YsrR
- PMID: 15205407
- PMCID: PMC421616
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.13.4056-4066.2004
Regulation of the Ysa type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica by YsaE/SycB and YsrS/YsrR
Abstract
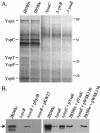
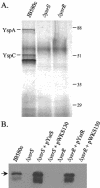
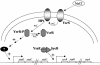
Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1B contains two type III secretion systems (TTSSs), the plasmid-encoded Ysc-Yop system and the chromosomally encoded Ysa-Ysp system. Proteins secreted from the Ysa TTSS (Ysps) have only been detected in vitro when cells are cultured at 26 degrees C in a high-NaCl medium. However, the exact role of the Ysa TTSS is unclear. Thus, investigations into the regulation of this system may help elucidate the role of the Ysps during the life cycle of Y. enterocolitica. Here we present evidence that the AraC-like regulator YsaE acts together with the chaperone SycB to regulate transcription of the sycByspBCDA operon, a phenomenon similar to that seen in the closely related Salmonella SPI-1 and Shigella flexneri Mxi-Spa-Ipa TTSSs. Deletion of either sycB or ysaE results in a twofold reduction in the activity of a sycB-lacZ fusion compared to the wild type. In a reconstituted Escherichia coli system, transcription of sycB was activated sixfold only when both YsaE and SycB were present, demonstrating that they are necessary for activation. ysrR and ysrS are located near the ysa genes and encode a putative two-component regulatory system. Mutations in either gene indicated that both YsrR and YsrS were required for secretion of Ysps. In addition, transcription from sycB-lacZ and ysaE-lacZ fusions was decreased 6.5- and 25-fold, respectively, in the ysrS mutant compared to the wild type. Furthermore, in the absence of NaCl, the activity of ysaE-lacZ was reduced 25-fold in the wild-type and DeltaysrS strains, indicating that YsrS is probably required for the salt-dependent expression of the ysa locus. These results suggest that the putative two-component system YsrRS may be a key element in the regulatory cascade for the Ysa TTSS.
Figures
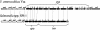

Similar articles
-
Synchronous gene expression of the Yersinia enterocolitica Ysa type III secretion system and its effectors.J Bacteriol. 2009 Mar;191(6):1816-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.01402-08. Epub 2009 Jan 5. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19124573 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the ysa pathogenicity locus in the chromosome of Yersinia enterocolitica and phylogeny analysis of type III secretion systems.J Mol Evol. 2002 Jul;55(1):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s00239-001-0089-7. J Mol Evol. 2002. PMID: 12165841
-
Identification of substrates and chaperone from the Yersinia enterocolitica 1B Ysa type III secretion system.Infect Immun. 2003 Jan;71(1):242-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.242-253.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12496172 Free PMC article.
-
The Ysa type 3 secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1B.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:286-97. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966425 Review.
-
Links between type III secretion and extracytoplasmic stress responses in Yersinia.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Oct 10;2:125. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00125. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23087910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein export according to schedule: architecture, assembly, and regulation of type III secretion systems from plant- and animal-pathogenic bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):262-310. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05017-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22688814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YspM, a newly identified Ysa type III secreted protein of Yersinia enterocolitica.J Bacteriol. 2008 Nov;190(22):7315-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.00861-08. Epub 2008 Sep 19. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18805975 Free PMC article.
-
YaxAB, a Yersinia enterocolitica pore-forming toxin regulated by RovA.Infect Immun. 2013 Nov;81(11):4208-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00781-13. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24002058 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of a YscY binding domain within the LcrH chaperone that is required for regulation of Yersinia type III secretion.J Bacteriol. 2005 Nov;187(22):7738-52. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.22.7738-7752.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16267298 Free PMC article.
-
IscR is essential for yersinia pseudotuberculosis type III secretion and virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jun 12;10(6):e1004194. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004194. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24945271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, P., C. A. Hart, and J. R. Saunders. 1987. Isolation from Klebsiella and characterization of two rcs genes that activate colanic acid capsular biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133:331-340. - PubMed
-
- Arricau, N., D. Hermant, H. Waxin, C. Ecobichon, P. S. Duffey, and M. Y. Popoff. 1998. The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol. Microbiol. 29:835-850. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Beloin, C., S. McKenna, and C. J. Dorman. 2002. Molecular dissection of VirB, a key regulator of the virulence cascade of Shigella flexneri. J. Biol. Chem. 277:15333-15344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

