Heterologous expression and purification of active divercin V41, a class IIa bacteriocin encoded by a synthetic gene in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15205430
- PMCID: PMC421597
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.13.4276-4284.2004
Heterologous expression and purification of active divercin V41, a class IIa bacteriocin encoded by a synthetic gene in Escherichia coli
Abstract
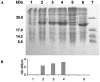
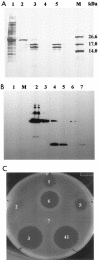
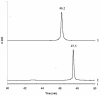
Divercin V41, a class IIa bacteriocin with strong antilisterial activity, is produced by Carnobacterium divergens V41. To express a recombinant version of divercin V41, we constructed a synthetic gene that encodes the mature divercin V41 peptide and then overexpressed the gene in pET-32b by using the T7 RNA polymerase promoter in the Escherichia coli Origami (DE3)(pLysS) strain. The DvnRV41 peptide was expressed as a translational fusion protein with thioredoxin and accumulated in the cell cytoplasm in a soluble anti-Listeria active form. The fusion protein was then purified and cleaved to obtain pure, soluble, folded DvnRV41 (462 microg per 20 ml of culture). This paper describes the first design of a synthetic bacteriocin gene and the first bacteriocin expressed in the E. coli cytoplasm.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Jun;70(2):564-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00016-05. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16760314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial activity of divercin RV41 produced and secreted by Lactococcus lactis.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;13(4):259-63. doi: 10.1159/000104756. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17827978
-
Insights into structure-activity relationships in the C-terminal region of divercin V41, a class IIa bacteriocin with high-level antilisterial activity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Apr;75(7):1811-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02266-08. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19181835 Free PMC article.
-
Production of recombinant bacteriocin divercin V41 by high cell density Escherichia coli batch and fed-batch cultures.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Dec;77(3):525-31. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1188-1. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17882416
-
Divercin V41 from gene characterization to food applications: 1998-2008, a decade of solved and unsolved questions.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2009 Jan;48(1):1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02490.x. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19018960 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of five class II bacteriocins with activity against Escherichia coli in Lacticaseibacillus paracasei CNCM I-5369, and in a heterologous host.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021 May 25;30:e00632. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00632. eCollection 2021 Jun. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34136365 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and functional expression of a food-grade circular bacteriocin, plantacyclin B21AG, in probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 12;15(8):e0232806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232806. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32785265 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo activities of recombinant divercin V41 and its structural variants against Listeria monocytogenes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):563-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00765-09. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 19841145 Free PMC article.
-
Mining and Statistical Modeling of Natural and Variant Class IIa Bacteriocins Elucidate Activity and Selectivity Profiles across Species.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Oct 28;86(22):e01646-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01646-20. Print 2020 Oct 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32917749 Free PMC article.
-
The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Jun;70(2):564-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00016-05. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16760314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baneyx, F. 1999. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 10:411-421. - PubMed
-
- Bellinzoni, M., E. De Rossi, M. Branzoni, A. Milano, F. A. Peverali, M. Rizzi, and G. Riccardi. 2002. Heterologous expression, purification, and enzymatic activity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NAD(+) synthetase. Protein Expr. Purif. 25:547-557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

