Sigma54 enhancer binding proteins and Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development
- PMID: 15205438
- PMCID: PMC421606
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.13.4361-4368.2004
Sigma54 enhancer binding proteins and Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development
Abstract
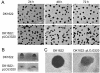
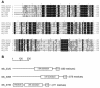
A search of the M1genome sequence, which includes 97% of the Myxococcus xanthus genes, identified 53 sequence homologs of sigma54-dependent enhancer binding proteins (EBPs). A DNA microarray was constructed from the M1genome that includes those homologs and 318 other M. xanthus genes for comparison. To screen the developmental program with this array, an RNA extract from growing cells was compared with one prepared from developing cells at 12 h. Previous reporter studies had shown that M. xanthus has initiated development and has begun to express many developmentally regulated genes by 12 h. The comparison revealed substantial increases in the expression levels of 11 transcription factors that may respond to environmental stimuli. Six of the 53 EBP homologs were expressed at significantly higher levels at 12 h of development than during growth. Three were previously unknown genes, and they were inactivated to look for effects on fruiting body development. One knockout mutant produced fruiting bodies of abnormal shape that depended on the composition of the medium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancer-binding proteins with a forkhead-associated domain and the sigma54 regulon in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):3010-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409371102. Epub 2005 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15668379 Free PMC article.
-
sigma54, a vital protein for Myxococcus xanthus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 4;94(5):1979-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.1979. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9050890 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted mutagenesis of sigma54 activator proteins in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 1998 Nov;180(22):5896-905. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.22.5896-5905.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9811647 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cell interactions that direct fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):363-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80301-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840894 Review.
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating pilin expression reveals a threshold for S motility in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2005 Mar;187(6):2105-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.6.2105-2112.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15743959 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of phase variation in Myxococcus xanthus.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Aug;81(3):784-804. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07732.x. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21722202 Free PMC article.
-
The Myxococcus xanthus developmental program can be delayed by inhibition of DNA replication.J Bacteriol. 2007 Dec;189(24):8793-800. doi: 10.1128/JB.01361-07. Epub 2007 Sep 28. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17905977 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Myxococcus xanthus Wild-Type Strain DZ2, a Model Organism for Predation and Development.Genome Announc. 2013 May 9;1(3):e00217-13. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00217-13. Genome Announc. 2013. PMID: 23661486 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic-like signaling and gene regulation in a prokaryote that undergoes multicellular development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2681-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500157102. Epub 2005 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15710872 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

