Effects of tetracycline on the pharmacokinetics of halofantrine in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 15206992
- PMCID: PMC1884545
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02087.x
Effects of tetracycline on the pharmacokinetics of halofantrine in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the effect of tetracycline co-administration on the pharmacokinetics of halofantrine in healthy subjects.
Methods: Eight healthy males were each given 500 mg single oral doses of halofantrine alone, or with tetracycline (500 mg 12 hourly for 7 days), in a crossover fashion. Blood samples collected at predetermined intervals were analyzed for halofantrine and its major metabolite, desbutylhalofantrine (HFM), using a validated HPLC method.
Results: Co-administration of tetracycline and halofantrine resulted in a significant increase (P < 0.05) in the maximum plasma concentration (C(max)), total area under the concentration-time curve (AUC), and terminal elimination half-life (t(1/2,z)), compared with halofantrine alone. (C(max) 0.43 +/- 0.14 vs 1.06 +/- 0.44 microg ml(-1) (95% CI on the difference 0.30, 0.95); AUC 32.0 +/- 13.6 vs 63.7 +/- 20.1 microg ml(-1) h (95% CI 14.2, 49.1); t(1/2,z:) 90.8 +/- 17.9 vs 157.4 +/- 57.4 h (95% CI 21.7, 111.5)). Similarly, tetracycline caused a significant increase (P < 0.05) in the AUC and C(max) of HFM.
Conclusions: Tetracycline co-administration significantly increases the plasma concentrations of halofantrine and its major metabolite.
Figures
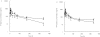
Similar articles
-
Effect of kolanut on the pharmacokinetics of the antimalarial drug halofantrine.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;64(1):77-81. doi: 10.1007/s00228-007-0387-0. Epub 2007 Oct 20. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17952423 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of halofantrine in healthy volunteers.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2009 Dec;34(6):677-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01064.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2009. PMID: 20175801 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of prior administration of amodiaquine on the disposition of halofantrine in healthy volunteers.Ther Drug Monit. 2007 Apr;29(2):203-6. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e31803d39f7. Ther Drug Monit. 2007. PMID: 17417075 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of halofantrine.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994 Aug;27(2):104-19. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199427020-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994. PMID: 7955774 Review.
-
Mechanism of cardiotoxicity of halofantrine.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000 May;67(5):521-9. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2000.106127. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10824631 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors affecting the electrocardiographic QT interval in malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data.PLoS Med. 2020 Mar 5;17(3):e1003040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003040. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32134952 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the integrated stress response confers vulnerability to mitoribosome-targeting antibiotics in melanoma.J Exp Med. 2021 Sep 6;218(9):e20210571. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210571. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34287642 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of kolanut on the pharmacokinetics of the antimalarial drug halofantrine.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;64(1):77-81. doi: 10.1007/s00228-007-0387-0. Epub 2007 Oct 20. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17952423 Clinical Trial.
-
Improving antibacterial prescribing safety in the management of COPD exacerbations: systematic review of observational and clinical studies on potential drug interactions associated with frequently prescribed antibacterials among COPD patients.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Oct 1;74(10):2848-2864. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz221. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31127283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wirima J, Molyneux ME, Khoromana C, Gilles HM. Clinical trials with halofantrine hydrochloride in Malawi. Lancet. 1988;ii:250–2. - PubMed
-
- Bryson HM, Goa K. Halofantrine: a review of its antimalarial activity, pharmacokinetics properties and therapeutic potentials. Drugs. 1992;43:236–58. - PubMed
-
- Karbwang J, Na Bangchang K. Clinical pharmacokinetics of halofantrine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994;27:104–19. - PubMed
-
- White NJ, Olliaro PL. Rationale for combination therapy for malaria. Parasitol Today. 1996;12:399–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

