99mTc glucarate high-resolution imaging of drug sensitive and drug resistant human breast cancer xenografts in SCID mice
- PMID: 15208499
- PMCID: PMC2946081
- DOI: 10.1097/01.mnm.0000130243.06821.90
99mTc glucarate high-resolution imaging of drug sensitive and drug resistant human breast cancer xenografts in SCID mice
Abstract
Background and aim: Previous studies have showed that 99mTc labelled glucarate (GLA) might be an agent for non-invasive detection of breast tumours. In xenografted BT20 breast tumours, GLA was found to have higher uptake than 99mTc sestamibi (MIBI). It is unclear whether GLA can localize in all cell line breast cancer xenografts, as well as breast tumours with multidrug resistance (MDR). The present study aimed to investigate the properties of GLA in detecting drug sensitive and drug resistant MCF7 breast cancer xenografts in mice by using dynamic single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging.
Methods: MCF7/S cells are drug sensitive breast carcinoma cells. MCF7/D40 cells are 40-fold more resistant to doxorubicin compared to MCF7/S. Subcutaneous tumours were grown in SCID mice for 10-14 days after injection of 1 x 10(6) cells into the right thigh. Anaesthetized mice with MCF7/S (MIBI, n=9; GLA, n=8) and MCF7/D40 (MIBI, n=6; GLA, n=5) tumours were imaged using a high-resolution SPECT system called FASTSPECT. Dynamic images were acquired for 2 h after intravenous injection of GLA or MIBI. Expression of MDR P-glycoprotein (Pgp) in the tumours was demonstrated in the MCF7/D40 tumours by western blotting, not in the MCF7/S tumours.
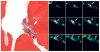
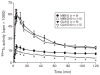
Results: The xenografted tumours were visualized unequivocally within 10-30 min in GLA images and remained detectable for at least 2 h after injection. Drug resistant tumours, from which MIBI was rapidly expelled, retained GLA as readily as did drug sensitive tumours. The biodistribution data of GLA demonstrated significantly higher accumulation (%ID/g) compared to MIBI.
Conclusion: MCF7 tumour xenografts can be detected by 99mTc glucarate imaging. More importantly, 99mTc glucarate can potentially localize drug resistant breast tumours.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Imaging recognition of inhibition of multidrug resistance in human breast cancer xenografts using 99mTc-labeled sestamibi and tetrofosmin.Nucl Med Biol. 2005 Aug;32(6):573-83. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2005.04.014. Nucl Med Biol. 2005. PMID: 16026704 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting human breast tumour in xeno-grafted SCID mice with 99Tcm-glucarate.Nucl Med Commun. 1997 Mar;18(3):241-51. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199703000-00008. Nucl Med Commun. 1997. PMID: 9106778
-
Investigations of (99m)Tc-labeled glucarate as a SPECT radiotracer for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and potential tumor uptake mechanism.Nucl Med Biol. 2015 Jul;42(7):608-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Nucl Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25890861
-
Dynamic imaging: scintimammography.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 2:S259-64. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00072-2. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652532 Review.
-
Scintigraphic detection of multidrug resistance in cancer.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2000 Aug;15(4):327-37. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2000.15.327. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2000. PMID: 11041017 Review.
Cited by
-
99mTc-Glucarate for assessment of paclitaxel therapy in human ovarian cancer in mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Jan;21(1):77-82. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.24707.6138. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29372040 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of uptake and retention of F-18 BMS-747158-02 in cardiomyocytes: a novel PET myocardial imaging agent.J Nucl Cardiol. 2007 Nov-Dec;14(6):782-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclcard.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Oct 22. J Nucl Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 18022104
-
Could 99mTc-glucarate be used to evaluate tumour necrosis? In vitro and in vivo studies in leukaemic tumour cell line U937.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008 Jul;35(7):1290-8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-007-0689-6. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18338166
-
Untiring Pursuit for Glucarate-Based Molecular Imaging Probes.Mol Imaging Biol. 2021 Jun;23(3):310-322. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01564-y. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Mol Imaging Biol. 2021. PMID: 33206335 Review.
-
(99m)Tc glucarate as a potential radiopharmaceutical agent for assessment of tumor viability: from bench to the bed side.World J Nucl Med. 2012 May;11(2):47-56. doi: 10.4103/1450-1147.103405. World J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 23372437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maublant J. Scintigraphic imaging of breast tumors. Eur J Radiology. 1997;24:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Buscombe JR, Cwikla JB, Thakrar DS, Hilson AJ. Scintigraphic imaging of breast cancer: a review. Nucl Med Commun. 1997;18:698–709. - PubMed
-
- Khalkhali I, Villanueva-Meyer J, Edell SL, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Baum JK, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-sestamibi breast imaging: multicenter trial results. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1973–1979. - PubMed
-
- Bennink RJ, Rijks LJ, van Tienhoven G, Noorduyn LA, Janssen AG, Sloof GW. Estrogen receptor status in primary breast cancer: iodine 123-labeled cis-11beta-methoxy-17alpha-iodovinyl estradiol scintigraphy. Radiology. 2001;220:774–779. - PubMed
-
- Ivancevic V, Wolter A, Winzer K, Aldinger H, Muller JM, Munz DL. Intraindividual comparison of F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose and Tc-99m-tetrofosmin in planar scintimammography and SPECT. Clin Positron Imaging. 2000;3:17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

