Mechanisms underlying differential expression of interleukin-8 in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 15208657
- PMCID: PMC2668865
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207815
Mechanisms underlying differential expression of interleukin-8 in breast cancer cells
Abstract
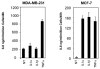
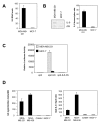
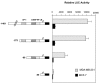
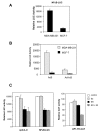
We have recently reported that interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression was inversely correlated to estrogen receptor (ER) status and was overexpressed in invasive breast cancer cells. In the present study, we show that IL-8 overexpression in breast cancer cells involves a higher transcriptional activity of IL-8 gene promoter. Cloning of IL-8 promoter from MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells expressing high and low levels of IL-8, respectively, shows the integrity of the promoter in both cell lines. Deletion and site-directed mutagenesis of the promoter demonstrate that NF-kappaB and AP-1 and to a lesser extent C/EBP binding sites play a crucial role in the control of IL-8 promoter activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. Knockdown of NF-kappaB and AP-1 activities by adenovirus-mediated expression of an NF-kappaB super-repressor and RNA interference, respectively, decreased IL-8 expression in MDA-MB-231 cells. On the contrary, restoration of Fra-1, Fra-2, c-Jun, p50, p65, C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta expression levels in MCF-7 cells led to a promoter activity comparable to that observed in MDA-MB-231 cells. Our data constitute the first extensive study of IL-8 gene overexpression in breast cancer cells and suggest that the high expression of IL-8 in invasive cancer cells requires a complex cooperation between NF-kappaB, AP-1 and C/EBP transcription factors.
Figures




References
-
- Bharti AC, Aggarwal BB. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:883–8. - PubMed
-
- Brew R, Southern SA, Flanagan BF, McDicken IW, Christmas SE. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A:2142–7. - PubMed
-
- Brown PH, Alani R, Preis LH, Szabo E, Birrer MJ. Oncogene. 1993;8:877–86. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer FA, Miller LJ, Andrawis RI, Kurtzman SH, Albertsen PC, Laudone VP, Kreutzer DL. Urology. 1998;51:161–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

