A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15208781
- PMCID: PMC1216068
- DOI: 10.1086/422827
A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
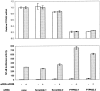
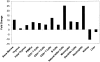
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common systemic autoimmune disease, affecting approximately 1% of the adult population worldwide, with an estimated heritability of 60%. To identify genes involved in RA susceptibility, we investigated the association between putative functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and RA among white individuals by use of a case-control study design; a second sample was tested for replication. Here we report the association of RA susceptibility with the minor allele of a missense SNP in PTPN22 (discovery-study allelic P=6.6 x 10(-4); replication-study allelic P=5.6 x 10(-8)), which encodes a hematopoietic-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase also known as "Lyp." We show that the risk allele, which is present in approximately 17% of white individuals from the general population and in approximately 28% of white individuals with RA, disrupts the P1 proline-rich motif that is important for interaction with Csk, potentially altering these proteins' normal function as negative regulators of T-cell activation. The minor allele of this SNP recently was implicated in type 1 diabetes, suggesting that the variant phosphatase may increase overall reactivity of the immune system and may heighten an individual carrier's risk for autoimmune disease.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PTPN22 major splice variant [accession number NM_015967])
-
- Genotype-IBD Sharing Test (GIST), http://phg.mc.vanderbilt.edu/GIST.shtml - PMC - PubMed
-
- New York Cancer Project, http://www.amdec.org
References
-
- Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Nika K, Rostamkhani M, MacMurray J, Meloni GF, Lucarelli P, Pellecchia M, Eisenbarth GS, Comings D, Mustelin T (2004) A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet 36:337–33810.1038/ng1323 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breslow NE, Day NE (1980) Statistical methods in cancer research, volume I: the analysis of case-control studies. IARC Sci Publ 32:5–338 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

