Cleavage of host keratin 8 by a Chlamydia-secreted protease
- PMID: 15213128
- PMCID: PMC427399
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.3863-3868.2004
Cleavage of host keratin 8 by a Chlamydia-secreted protease
Abstract
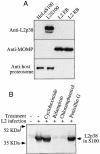
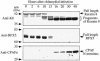
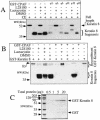
Chlamydiae have to replicate within a cytoplasmic vacuole in eukaryotic cells. Expansion of the chlamydia-laden vacuole is essential for chlamydial intravacuolar replication, which inevitably causes host cell cytoskeleton rearrangements. A cleavage fragment of keratin 8 corresponding to the central rod region was detected in the soluble fraction of chlamydia-infected cells. Since keratin 8 is a major component of the intermediate filaments in simple epithelial cells, cleavage of keratin 8 may increase the solubility of the host cell cytoskeleton and thus permit vacuole expansion in chlamydia-infected cells. A chlamydia-secreted protease designated CPAF (chlamydial protease/proteasome-like activity factor) was both necessary and sufficient for keratin 8 cleavage in chlamydia-infected cells, suggesting that chlamydiae have evolved specific mechanisms for modifying the host cell cytoskeleton.
Figures


References
-
- Casanova, L., A. Bravo, F. Were, A. Ramirez, J. J. Jorcano, and M. Vidal. 1995. Tissue-specific and efficient expression of the human simple epithelial keratin 8 gene in transgenic mice. J. Cell Sci. 108:811-820. - PubMed
-
- Ditzel, H. J., M. C. Strik, M. K. Larsen, A. C. Willis, A. Waseem, K. Kejling, and J. C. Jensenius. 2002. Cancer-associated cleavage of cytokeratin 8/18 heterotypic complexes exposes a neoepitope in human adenocarcinomas. J. Biol. Chem. 277:21712-21722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

