Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin is critical for lung infection in mice
- PMID: 15213173
- PMCID: PMC427412
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4275-4278.2004
Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin is critical for lung infection in mice
Abstract
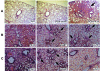
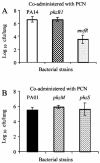
Pseudomonas aeruginosa secretes copious amounts of the redox-active phenazine, pyocyanin (PCN), during cystic fibrosis lung infection. PCN has been shown to interfere with a variety of cellular processes in cultured lung epithelial cells. Here, by using two respiratory tract models of infection, we demonstrate that PCN mediates tissue damage and necrosis during lung infection.
Figures


References
-
- Chiang, S. L., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1998. Use of signature-tagged transposon mutagenesis to identify Vibrio cholerae genes critical for colonization. Mol. Microbiol. 27:797-805. - PubMed
-
- Denning, G. M., M. A. Railsback, G. T. Rasmussen, C. D. Cox, and B. E. Britigan. 1998. Pseudomonas pyocyanine alters calcium signaling in human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 274:L893-L900. - PubMed
-
- Frank, D. W. 1997. The exoenzyme S regulon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 26:621-629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

