Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, apomucins, matrix metalloproteinases, and p53 in rat and human cholangiocarcinoma: appraisal of an animal model of cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 15213623
- PMCID: PMC1356379
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000129492.95311.f2
Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, apomucins, matrix metalloproteinases, and p53 in rat and human cholangiocarcinoma: appraisal of an animal model of cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: We sought to determine the expression of molecular markers in an animal model of cholangiocarcinoma compared with those in human cholangiocarcinoma.
Summary background data: Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare disease characterized by early intrahepatic and extrahepatic spread, which seriously limits the efficacy of surgery. Establishing an experimental model to study the cholangiocarcinogenesis is desirable.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 300 +/- 50 g were used for the study group. The animals were given 0.3% thioacetamide in tap water continuously. Thirty mass-forming peripheral cholangiocarcinoma patients also were studied. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, MMP-2, MMP-9, and p53 in both human and experimental rat cholangiocarcinoma was examined using immunohistochemistry.
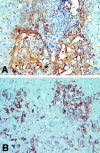
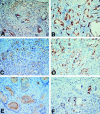
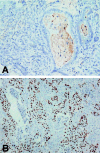
Results: Using thioacetamide 0.3% as a hepatoxin to induce cholangiocarcinoma in rats, microfoci of cancerous cells were detected from 12 weeks, and all experimental rats displayed diffuse mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma after 24 weeks. EGFR was strongly expressed in 14 (47%) of 30 human cholangiocarcinoms and 24 (100%) of 24 rat cholangiocarcinomas, respectively. MUC1 was strongly expressed in all human and rat cholangiocarcinomas, whereas MUC2 and MUC5AC were focally and weakly expressed. MMP-2 and MMP-9 were strongly expressed in 22 (73%) of 30 human cholangiocarcinomas and 24 (100%) of 24 rat cholangiocarcinomas, respectively. p53 overexpression was detected in 9 (30%) of 30 human cholangiocarcinoma and none of the rat cholangiocarcinoma, respectively.
Conclusions: The expression of EGFR, apomucins, MMPs, and p53 in rat cholangiocarcinoma was strongly homologous to human cholangiocarcinoma. Thioacetamide-induced cholangiocarcinoma in rats provides an excellent model for investigating cholangiocarcinogenesis in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Chen MF, Jan YY, Wang CS, et al. Intrahepatic duct stone associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989;84:391–395. - PubMed
-
- Chen MF, Jan YY, Wang CS, et al. A reappraisal of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with hepatolithiasis. Cancer. 1993;71:2461–2465. - PubMed
-
- Yeh TS, jan YY, Tseng JH, et al. Malignant perihilar biliary obstruction: magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatographic findings. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:432–440. - PubMed
-
- Jan YY, Yeh TS, Chen MF. Cholangiocarcinoma presenting as pyogenic liver abscess. Is its outcome influenced by concomitant hepatolithiasis? Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:253–255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

