In vitro activities of a novel cephalosporin, CB-181963 (CAB-175), against methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus and glycopeptide-intermediate susceptible staphylococci
- PMID: 15215134
- PMCID: PMC434184
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.7.2719-2723.2004
In vitro activities of a novel cephalosporin, CB-181963 (CAB-175), against methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus and glycopeptide-intermediate susceptible staphylococci
Abstract
We examined the activity of CB-181963, a novel cephalosporin, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (n = 200), methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) (n = 50), glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus species (GISS) (n = 47), and VRSA (n = 2) isolates. CB-181963 exhibited MIC profiles similar to those of linezolid against MRSA and GISS; however, activity against MSSA was similar to that of vancomycin. Time-kill study results of investigations of activity against MRSA, MSSA, and GISS at 24 h were as follows: CB-181963 activity = vancomycin activity > linezolid activity (P < 0.001); CB-181963 = quinupristin-dalfopristin = vancomycin > linezolid (P < 0.05); CB-181963 > linezolid (P = 0.003); and CB-181963 = quinupristin-dalfopristin = vancomycin. CB-181963 may provide an alternative treatment for multidrug-resistant staphylococci.
Figures
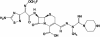


References
-
- Ariza, J., M. Pujol, J. Cabo, C. Pena, N. Fernandez, T. Linares, J. Ayats, and F. Gudiol. 1999. Vancomycin in surgical infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin. Lancet 353:1587-1588. - PubMed
-
- Bert, F., J. Clarissou, F. Durand, D. Delefosse, C. Chauvet, P. Lefebvre, N. Lambert, and C. Branger. 2003. Prevalence, molecular epidemiology, and clinical significance of heterogeneous glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in liver transplant recipients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:5147-5152. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bierbaum, G., K. Fuchs, W. Lenz, and H.-G. Sahl. 1999. Presence of Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin in Germany. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 18:691-696. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1996. Reduced susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to vancomycin—Japan 1996. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 46:624-626. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—United States, 1997. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 46:765-766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

