Soluble receptor (DcR3) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-2 (cIAP-2) protect human cytotrophoblast cells against LIGHT-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 15215185
- PMCID: PMC1618528
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63298-1
Soluble receptor (DcR3) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-2 (cIAP-2) protect human cytotrophoblast cells against LIGHT-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
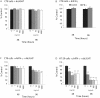
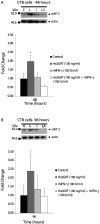
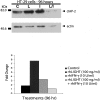
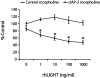
LIGHT (tumor necrosis factor superfamily 14) is among the powerful apoptosis-inducing cytokines synthesized in human placentas. Here, we investigated mechanisms protecting cytotrophoblast (CTB) cells from LIGHT-mediated apoptosis. Viability assays and caspase-3 immunoblots using recombinant LIGHT were done to establish that CTB cells purified from term placentas resist LIGHT-induced apoptosis. Although the cells were also resistant to killing by another placental cytokine, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), a combination of the two induced apoptosis. Killing was prevented by DcR3-Fc fragment but not control human-Fc fragment, showing that apoptosis occurs via the LIGHT pathway and that soluble receptors provide protection. Next, two cellular inhibitors of apoptosis expressed in CTB cells, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis (cIAP)-1 and cIAP-2, were investigated for protection. Cellular IAP-1 was unchanged after stimulation with LIGHT whereas cIAP-2 mRNA and protein were elevated. The increase was abrogated by treating CTB cells with LIGHT + IFN-gamma, implying a central role for cIAP-2 in preventing LIGHT-mediated apoptosis and an ability of IFN-gamma to overcome cIAP-2 protection. Definitive evidence was provided in experiments that showed that cIAP-2 anti-sense morpholinos permit LIGHT to induce apoptosis in HT-29 cells. In summary, the data are consistent with the postulate that placental CTB cells are protected from LIGHT-mediated apoptosis by both soluble receptor, DcR3, and cIAP-2.
Figures



References
-
- Phillips TA, Ni J, Hunt JS. Death-inducing tumour necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily ligands and receptors are transcribed in human placentae, cytotrophoblasts, placental macrophages and placental cell lines. Placenta. 2001;22:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Tamada K, Shimozaki K, Chapoval AI, Zhai Y, Su J, Chen S, Hsieh S, Nagata S, Ni J, Chen L. LIGHT, a TNF-like molecule, costimulates T cell proliferation and is required for dendritic cell-mediated allogenic T cell response. J Immunol. 2000;164:4105–4110. - PubMed
-
- Morel Y, Schiano de Colella J, Harrop J, Deen KC, Holmes SD, Wattam TA, Khandejar SS, Truneh A, Sweet RW, Gastaut J, Olive D, Costello RT. Reciprocal expression of the TNF family receptor herpes virus entry mediator and its ligand LIGHT on activated T cells: LIGHT downregulates its own receptors. J Immunol. 2000;165:4397–4404. - PubMed
-
- Granger SW, Butrovich KD, Houshmand P, Edwards WR, Ware CF. Genomic characterization of LIGHT reveals linkage to an immune response locus on chromosome 19p13.3 and distinct isoforms generated by alternate splicing or proteolysis. J Immunol. 2001;167:5122–5128. - PubMed
-
- Harrop JA, McDonnell PC, Brigham-Burke M, Lyn SD, Minton J, Tan KB, Dede K, Spampanato J, Silverman C, Hensley P, DiPrinzio R, Emery JG, Deen K, Eichman C, Chabot-Fletcher M, Truneh A, Young P. Herpesvirus entry mediator ligand (HVEM-L), a novel ligand for HVEM/TR2, stimulates proliferation of T-cells and inhibits HT29 cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:27548–27556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

