siRNA Selection Server: an automated siRNA oligonucleotide prediction server
- PMID: 15215365
- PMCID: PMC441504
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh366
siRNA Selection Server: an automated siRNA oligonucleotide prediction server
Abstract
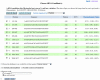
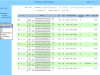
The Whitehead siRNA (short interfering RNA) Selection Web Server (http://jura.wi.mit.edu/bioc/siRNA) automates the design of short oligonucleotides that can specifically 'knock down' expression of target genes. These short sequences are about 21 nt in length, and when synthesized as double stranded RNA and introduced into cell culture, can reduce or eliminate the function of the target gene. Depending on the length of a gene, there are potentially numerous combinations of possible 21mers. Some experimental evidence has already shown that not all 21mers in a gene have the same effectiveness at silencing gene function. Our tool incorporates published design rules and presents the scientist with information about uniqueness of the 21mers within the genome, thermodynamic stability of the double stranded RNA duplex, GC content, presence of SNPs and other features that may contribute to the effectiveness of a siRNA.
Figures
References
-
- Dykxhoorn D.M., Novina,C.D. and Sharp,P.A. (2003) Killing the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 4, 457–467. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir S.M., Harborth,J., Lendeckel,W., Yalcin,A., Waber,K. and Tuschl,T. (2001) Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature, 411, 494–498. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir S.M., Harborth,J., Weber,K. and Tuschl,T. (2002) Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Methods, 26, 199–213. - PubMed
-
- Harborth J., Elbashir,S.M., Vandenburgh,K., Manninga,H., Scaringe,S.A., Weber,K. and Tuschl,T. (2003) Sequence, chemical, and structural variation of small interfering RNAs and short hairpin RNAs and the effect on mammalian gene silencing. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev., 13, 83–105. - PubMed
-
- Tuschl T. (2002) Expanding small RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 446–448. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous