CHOP: parsing proteins into structural domains
- PMID: 15215452
- PMCID: PMC441619
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh481
CHOP: parsing proteins into structural domains
Abstract
Sequence-based domain assignment is one of the most important and challenging problems in structural biology. We have developed a method, CHOP, that chops proteins into domain-like fragments. The basic idea is to cut proteins from entirely sequenced organisms beginning from very reliable experimental information (Protein Data Bank), proceeding to expert annotations of domain-like regions (Pfam-A) and completing through cuts based on termini of native protein ends. The CHOP server takes protein sequences as input and returns the dissections supported by homology transfer. CHOP results are precompiled for many entirely sequenced proteomes. The service is available at http://www.rostlab.org/services/CHOP/.
Figures
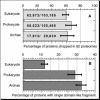
References
-
- Liu J. and Rost,B. (2003) Domains, motifs, and clusters in the protein universe. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 7, 5–11. - PubMed
-
- Liu J. and Rost,B. (2004) CHOP proteins into structural domain-like fragments. Proteins, 55, 678–688. - PubMed
-
- Liu J., Acton,T., Goldsmith,S., Honig,B., Montelione,G.T. and Rost,B. (2004) Automatic target selection for structural genomics on eukaryotes. Proteins (in press). - PubMed
-
- Yang A.S. and Honig,B. (2000) An integrated approach to the analysis and modeling of protein sequences and structures. II. On the relationship between sequence and structural similarity for proteins that are not obviously related in sequence. J. Mol. Biol., 301, 679–689. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

