EMD273316 & EMD95833, type 4 phosphodiesterase inhibitors, stimulate fibroblastic-colony formation by bone marrow cells via direct inhibition of PDE4 and the induction of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis
- PMID: 15219232
- PMCID: PMC449707
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-4-10
EMD273316 & EMD95833, type 4 phosphodiesterase inhibitors, stimulate fibroblastic-colony formation by bone marrow cells via direct inhibition of PDE4 and the induction of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis
Abstract
Background: Type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4) inhibitors have been shown to stimulate bone formation in vivo and to stimulate osteoblastic differentiation in vitro. As one possible mechanism for the stimulation of bone formation is the recruitment of osteoprogenitor cells from the bone marrow, we have investigated the effect of the PDE4 inhibitors EMD273316, EMD95833, EMD249615 and EMD 219906 on fibroblastic colony formation by whole bone marrow cells and on the ability of these colonies to adopt an osteoblastic phenotype.
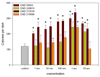
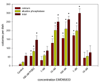
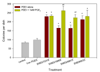
Results: All four agents stimulated colony formation in a concentration dependent manner, however, in the case of EMD273316 & EMD95833, the effect was evident at lower concentrations and the addition of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was not necessary for maximal stimulation. It was subsequently found that co-incubation with indomethacin reduced the stimulatory effects of EMD273316 & EMD95833 but had no effect on the actions of EMD249615 and EMD 219906 and that EMD273316 & EMD95833 stimulated the synthesis of endogenous PGE2 by whole bone marrow cells whereas EMD249615 and EMD 219906 had no significant effect.
Conclusions: These data suggest that EMD249615, EMD 219906, EMD273316 & EMD95833 can promote the recruitment of bone marrow osteoprogenitor cells leading to a stimulation of bone formation via their direct inhibitory effects on PDE4. The actions of EMD273316 & EMD95833 however, are augmented by their ability to stimulate endogenous prostanoids synthesis which acts synergistically with their direct effects on PDE4.
Figures


References
-
- Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: functional implications of multiple isoforms. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:725–48. - PubMed
-
- Kasugai S, Miyamoto K. Potential of PDE4 inhibitors in the treatment of osteopenia. Drug News and Perspectives. 1999;12:529–534.
-
- Wakabayashi S, Tsutsumimoto T, Kinoshita T, Horiuchi H, Takaoka K. Effect of selective inhibitors for phosphodiesterase on the osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow-derived stromal cell. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15:M198.
-
- Scutt A, Still K, Reading L, Fittschen C. Effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on fibroblastic colony formation in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15:P10.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

