The phenylmethylthiazolylthiourea nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitor MSK-076 selects for a resistance mutation in the active site of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 RT
- PMID: 15220416
- PMCID: PMC434123
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7427-7437.2004
The phenylmethylthiazolylthiourea nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitor MSK-076 selects for a resistance mutation in the active site of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 RT
Abstract
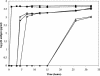
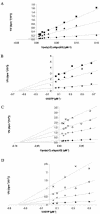
The phenylmethylthiazolylthiourea (PETT) derivative MSK-076 shows, besides high potency against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), marked activity against HIV-2 (50% effective concentration, 0.63 microM) in cell culture. Time-of-addition experiments pointed to HIV-2 reverse transcriptase (RT) as the target of action of MSK-076. Recombinant HIV-2 RT was inhibited by MSK-076 at 23 microM. As was also found for HIV-1 RT, MSK-076 inhibited HIV-2 RT in a noncompetitive manner with respect to dGTP and poly(rC).oligo(dG) as the substrate and template-primer, respectively. MSK-076 selected for A101P and G112E mutations in HIV-2 RT and for K101E, Y181C, and G190R mutations in HIV-1 RT. The selected mutated strains of HIV-2 were fully resistant to MSK-076, and the mutant HIV-2 RT enzymes into which the A101P and/or G112E mutation was introduced by site-directed mutagenesis showed more than 50-fold resistance to MSK-076. Mapping of the resistance mutations to the HIV-2 RT structure ascertained that A101P is located at a position equivalent to the nonnucleoside RT inhibitor (NNRTI)-binding site of HIV-1 RT. G112E, however, is distal to the putative NNRTI-binding site in HIV-2 RT but close to the active site, implying a novel molecular mode of action and mechanism of resistance. Our findings have important implications for the development of new NNRTIs with pronounced activity against a wider range of lentiviruses.
Figures


References
-
- Ahgren, C., K. Backbro, F. W. Bell, A. S. Cantrell, M. Clemens, J. M. Colacino, J. B. Deeter, J. A. Engelhardt, M. Hogberg, S. R. Jaskunas, N. G. Johansson, C. L. Jordan, J. S. Kasher, M. D. Kinnick, P. Lind, C. Lopez, J. M. Morin, Jr., M. A. Muesing, R. Noreen, B. Öberg, C. J. Paget, J. A. Palkowitz, C. A. Parrish, P. Pranc, M. K. Rippy, C. Rydergard, C. Sahlberg, S. Swanson, R. J. Ternansky, T. Unge, R. T. Vasileff, L. Vrang, S. J. West, H. Zhang, and X. X. Zhou. 1995. The PETT series, a new class of potent nonnucleoside inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39:1329-1335. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., H. Tanaka, E. De Clercq, R. Pauwels, J. Balzarini, D. Schols, H. Nakashima, C. F. Perno, R. T. Walker, and T. Miyasaka. 1989. Highly specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by a novel 6-substituted acyclouridine derivative. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 165:1375-1381. - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., M. Okamoto, M. Kawamura, M. Makino, T. Higashida, T. Takashi, Y. Kimura, T. Ikeuchi, T. Tetsuka, and T. Okamoto. 1998. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication and cytokine production by fluoroquinoline derivatives. Mol. Pharmacol. 53:1097-1103. - PubMed
-
- Bacolla, A., C. K. Shih, J. M. Rose, G. Piras, T. C. Warren, C. A. Grygon, R. H. Ingraham, R. C. Cousins, D. J. Greenwood, D. Richman, Y.-C. Cheng, and J. A. Griffin. 1993. Amino acid substitutions in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with corresponding residues from HIV-2. Effect on kinetic constants and inhibition by non-nucleoside analogs. J. Biol. Chem. 268:16571-16577. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini, J., M. J. Péréz-Péréz, A. San-Félix, M. J. Camarasa, I. C. Bathurst, P. J. Barr, and E. De Clercq. 1992. Kinetics of inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase by the novel HIV-1-specific nucleoside analogue [2′,5′-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-β-d-ribofuranosyl]-3′-spiro-5"-(4"-amino-1",2"-oxathiole-2",2"-dioxide) thymine (TSAO-T). J. Biol. Chem. 267:11831-11838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

