Three novel cis-acting elements required for efficient plus-strand DNA synthesis of the hepatitis B virus genome
- PMID: 15220419
- PMCID: PMC434075
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7455-7464.2004
Three novel cis-acting elements required for efficient plus-strand DNA synthesis of the hepatitis B virus genome
Abstract
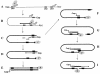
Synthesis of the relaxed-circular (RC) DNA genomes of hepadnaviruses by reverse transcriptase involves two template switches during plus-strand DNA synthesis. These template switches require repeat sequences (so-called donor and acceptor sites) between which a complementary strand of nucleic acid is transferred. To determine cis-acting elements apart from the donor and acceptor sites that are required for plus-strand RC DNA synthesis by hepatitis B virus (HBV), a series of mutants bearing a small deletion were made and analyzed for their impact on the viral genome synthesis. We found three novel cis-acting elements in the HBV genome: one element, located in the middle of the minus strand, is indispensable, whereas the other two elements, located near either end of the minus strand, contribute modestly to the plus-strand RC DNA synthesis. The data indicated that the first element facilitates plus-strand RNA primer translocation or subsequent elongation during plus-strand RC DNA synthesis, while the last two elements, although distantly located on the minus strand, act at multiple steps to promote plus-strand RC DNA synthesis. The necessity of multiple cis-acting elements on the minus-strand template reflects the complex nature of hepadnavirus reverse transcription.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel cis-acting element facilitates minus-strand DNA synthesis during reverse transcription of the hepatitis B virus genome.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6252-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6252-6262.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163718 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Acting sequences in addition to donor and acceptor sites are required for template switching during synthesis of plus-strand DNA for duck hepatitis B virus.J Virol. 1997 Jul;71(7):5336-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.7.5336-5344.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9188603 Free PMC article.
-
Circularization of an RNA template via long-range base pairing is critical for hepadnaviral reverse transcription.Virology. 2008 Feb 20;371(2):362-73. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.042. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Virology. 2008. PMID: 17988705
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and its many roles in hepadnaviral genomic replication.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):85-93. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7529120 Review.
-
'Binding, bending and bonding': polypurine tract-primed initiation of plus-strand DNA synthesis in human immunodeficiency virus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;36(9):1752-66. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.02.016. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15183342 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA on oncogenesis and antiviral therapy.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 15;12(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00611-y. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39148134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus replication.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 7;13(1):48-64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17206754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Base pairing between cis-acting sequences contributes to template switching during plus-strand DNA synthesis in human hepatitis B virus.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6207-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00210-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17409141 Free PMC article.
-
HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Viruses. 2017 Apr 10;9(4):75. doi: 10.3390/v9040075. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28394272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DDX3 DEAD-Box RNA helicase inhibits hepatitis B virus reverse transcription by incorporation into nucleocapsids.J Virol. 2009 Jun;83(11):5815-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00011-09. Epub 2009 Mar 18. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19297497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Condreay, L. D., T. T. Wu, C. E. Aldrich, M. A. Delaney, J. Summers, C. Seeger, and W. S. Mason. 1992. Replication of DHBV genomes with mutations at the sites of initiation of minus- and plus-strand DNA synthesis. Virology 188:208-216. - PubMed
-
- Galibert, F., E. Mandart, F. Fitoussi, P. Tiollais, and P. Charnay. 1979. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature 281:646-650. - PubMed
-
- Ganem, D., and R. Schneider. 2001. Hepadnaviridae: the viruses and their replication, 4th ed., vol. 2. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Goff, S. 2001. Retroviridae: the retroviruses and their replication, p. 1871-1939. In P. M. Hawley and D. M. Knipe (ed.), Field's virology, 4th ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

