Gain of virulence caused by loss of a gene in murine cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 15220428
- PMCID: PMC434107
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7536-7544.2004
Gain of virulence caused by loss of a gene in murine cytomegalovirus
Abstract
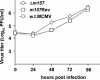
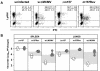
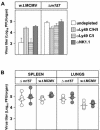
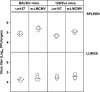
Mouse strains are either resistant or susceptible to murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV). Resistance is determined by the Cmv1(r) (Ly49h) gene, which encodes the Ly49H NK cell activation receptor. The protein encoded by the m157 gene of MCMV has been defined as a ligand for Ly49H. To find out whether the m157 protein is the only Ly49H ligand encoded by MCMV, we constructed the m157 deletion mutant and a revertant virus. Viruses were tested for susceptibility to NK cell control in Ly49H+ and Ly49H- mouse strains. Deletion of the m157 gene abolished the viral activation of Ly49H+ NK cells, resulting in higher virus virulence in vivo. Thus, in the absence of m157, Ly49H+ mice react like susceptible strains. 129/SvJ mice lack the Ly49H activation NK cell receptor but express the inhibitory Ly49I NK cell receptor that binds to the m157 protein. The Deltam157 inhibitory phenotype was weak because MCMV encodes a number of proteins that mediate NK inhibition, whose contribution could be shown by another mutant.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors.Science. 2002 May 17;296(5571):1323-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1070884. Epub 2002 Apr 11. Science. 2002. PMID: 11950999
-
Continuous engagement of a self-specific activation receptor induces NK cell tolerance.J Exp Med. 2008 Aug 4;205(8):1829-41. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072446. Epub 2008 Jul 7. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18606857 Free PMC article.
-
Functional consequences of natural sequence variation of murine cytomegalovirus m157 for Ly49 receptor specificity and NK cell activation.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 1;186(3):1713-22. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003308. Epub 2010 Dec 27. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21187440
-
Genetic control of innate immune responses against cytomegalovirus: MCMV meets its match.Genes Immun. 2002 Aug;3(5):250-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363876. Genes Immun. 2002. PMID: 12140743 Review.
-
Cmv1 and natural killer cell responses to murine cytomegalovirus infection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;321:101-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75203-5_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18727489 Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immunity regulates adaptive immune response: lessons learned from studying the interplay between NK and CD8+ T cells during MCMV infection.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2012 Nov;201(4):487-95. doi: 10.1007/s00430-012-0263-0. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22965169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cells as an initial defense against pathogens.Curr Opin Immunol. 2006 Aug;18(4):391-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2006.05.002. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16765573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inducible down-regulation of MHC class I results in natural killer cell tolerance.J Exp Med. 2019 Jan 7;216(1):99-116. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181076. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 30559128 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Deficiency Facilitates TNF-α-Dependent Hepatocyte Death and Liver Inflammation in MCMV Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 8;10:185. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00185. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30800112 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells in immunodefense against infective agents.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008 Dec;6(6):867-85. doi: 10.1586/14787210.6.6.867. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008. PMID: 19053900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arase, H., and L. L. Lanier. 2002. Virus-driven evolution of natural killer cell receptors. Microbes Infect. 4:1505-1512. - PubMed
-
- Arase, H., E. S. Mocarski, A. E. Campbell, A. B. Hill, and L. L. Lanier. 2002. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science 296:1323-1326. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, S., V. Groh, J. Wu, A. Steinle, J. H. Phillips, L. L. Lanier, and T. Spies. 1999. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 285:727-729. - PubMed
-
- Biron, C. A., K. B. Nguyen, G. C. Pien, L. P. Cousens, and T. P. Salazar-Mather. 1999. Natural killer cells in antiviral defense: function and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:189-220. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. G., A. O. Dokun, J. W. Heusel, H. R. Smith, D. L. Beckman, E. A. Blattenberger, C. E. Dubbelde, L. R. Stone, A. A. Scalzo, and W. M. Yokoyama. 2001. Vital involvement of a natural killer cell activation receptor in resistance to viral infection. Science 292:934-937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

