Phosphorylation of Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA protein at its casein kinase 2 sites mediates its ability to repress activation of a viral lytic cycle late gene by Rta
- PMID: 15220438
- PMCID: PMC434091
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7634-7644.2004
Phosphorylation of Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA protein at its casein kinase 2 sites mediates its ability to repress activation of a viral lytic cycle late gene by Rta
Abstract
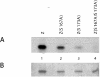
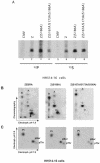
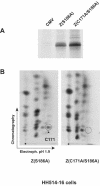
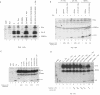
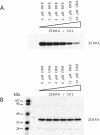
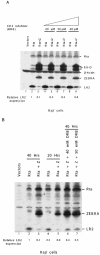
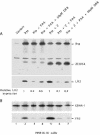
ZEBRA, a member of the bZIP family, serves as a master switch between latent and lytic cycle Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gene expression. ZEBRA influences the activity of another viral transactivator, Rta, in a gene-specific manner. Some early lytic cycle genes, such as BMRF1, are activated in synergy by ZEBRA and Rta. However, ZEBRA suppresses Rta's ability to activate a late gene, BLRF2. Here we show that this repressive activity is dependent on the phosphorylation state of ZEBRA. We find that two residues of ZEBRA, S167 and S173, that are phosphorylated by casein kinase 2 (CK2) in vitro are also phosphorylated in vivo. Inhibition of ZEBRA phosphorylation at the CK2 substrate motif, either by serine-to-alanine substitutions or by use of a specific inhibitor of CK2, abolished ZEBRA's capacity to repress Rta activation of the BLRF2 gene, but did not alter its ability to initiate the lytic cycle or to synergize with Rta in activation of the BMRF1 early-lytic-cycle gene. These studies illustrate how the phosphorylation state of a transcriptional activator can modulate its behavior as an activator or repressor of gene expression. Phosphorylation of ZEBRA at its CK2 sites is likely to play an essential role in proper temporal control of the EBV lytic life cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino acid substitutions reveal distinct functions of serine 186 of the ZEBRA protein in activation of early lytic cycle genes and synergy with the Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator.J Virol. 1999 Jun;73(6):4543-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.4543-4551.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10233912 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the epstein-barr virus RTA protein in activation of distinct classes of viral lytic cycle genes.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):9858-66. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9858-9866.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559298 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
-
Phosphoacceptor site S173 in the regulatory domain of Epstein-Barr Virus ZEBRA protein is required for lytic DNA replication but not for activation of viral early genes.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(7):3303-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02445-06. Epub 2007 Jan 10. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17215287 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cellular and viral protein expression by the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptional regulator Zta: implications for therapy of EBV associated tumors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jun;8(11):987-95. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.11.8369. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19448399 Review.
Cited by
-
Latency of Epstein-Barr virus is disrupted by gain-of-function mutant cellular AP-1 proteins that preferentially bind methylated DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 14;110(20):8176-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301577110. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23625009 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LF2 protein regulates viral replication by altering Rta subcellular localization.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(19):9920-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00573-10. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20631124 Free PMC article.
-
The human adenovirus type 5 E1B 55-kilodalton protein is phosphorylated by protein kinase CK2.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(5):2400-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06066-11. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22190719 Free PMC article.
-
Ser-634 and Ser-636 of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus RTA are Involved in Transactivation and are Potential Cdk9 Phosphorylation Sites.Front Microbiol. 2012 Feb 22;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00060. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22371709 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting CK2 beta-dependent substrates using linear patterns.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015 Aug 20;4:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.08.011. eCollection 2015 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015. PMID: 29124183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamson, A. L., and S. C. Kenney. 1998. Rescue of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 mutant, Z(S186A), early gene activation defect by the BRLF1 gene product. Virology 251:187-197. - PubMed
-
- Beral, V., T. Peterman, R. Berkelman, and H. Jaffe. 1991. AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet 337:805-809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

