Replication of herpes simplex virus 1 depends on the gamma 134.5 functions that facilitate virus response to interferon and egress in the different stages of productive infection
- PMID: 15220440
- PMCID: PMC434106
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7653-7666.2004
Replication of herpes simplex virus 1 depends on the gamma 134.5 functions that facilitate virus response to interferon and egress in the different stages of productive infection
Abstract
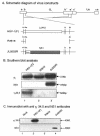
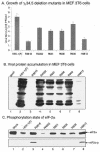
The ability of the gamma(1)34.5 protein to suppress the PKR response plays a crucial role in herpes simplex virus pathogenesis. In this process, the gamma(1)34.5 protein associates with protein phosphatase 1 to form a large complex that dephosphorylates eIF-2alpha and thereby prevents translation shutoff mediated by PKR. Accordingly, gamma(1)34.5 null mutants are virulent in PKR-knockout mice but not in wild-type mice. However, gamma(1)34.5 deletion mutants, with an extragenic compensatory mutation, inhibit PKR activity but remain avirulent, suggesting that the gamma(1)34.5 protein has additional functions. Here, we show that a substitution of the gamma(1)34.5 gene with the NS1 gene from influenza A virus renders viral resistance to interferon involving PKR. The virus replicates as efficiently as wild-type virus in SK-N-SH and CV-1 cells. However, in mouse 3T6 cells, the virus expressing the NS1 protein grows at an intermediate level between the wild-type virus and the gamma(1)34.5 deletion mutant. This decrease in growth, compared to that of the wild-type virus, is due not to an inhibition of viral protein synthesis but rather to a block in virus release or egress. Virus particles are predominantly present in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Notably, deletions in the amino terminus of the gamma(1)34.5 protein lead to a significant decrease in virus growth in mouse 3T6 cells, which is independent of eIF-2alpha dephosphorylation. In correlation, a series of deletions in the amino-terminal domain impair nuclear as well as cytoplasmic egress. These results indicate that efficient viral replication depends on the gamma(1)34.5 functions required to prevent the PKR response and to facilitate virus egress in the different stages during virus infection.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Second-site mutation outside of the U(S)10-12 domain of Deltagamma(1)34.5 herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant blocks the shutoff of protein synthesis induced by activated protein kinase R and partially restores neurovirulence.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(3):942-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.3.942-949.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11773369 Free PMC article.
-
Dephosphorylation of eIF-2alpha mediated by the gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for viral response to interferon but is not sufficient for efficient viral replication.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(18):10154-61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.10154-10161.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12941928 Free PMC article.
-
Val193 and Phe195 of the gamma 1 34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 are required for viral resistance to interferon-alpha/beta.Virology. 2001 Nov 10;290(1):115-20. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1148. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11882996
-
HSV gene functions: what have we learned that could be generally applicable to its near and distant cousins?Acta Virol. 1999 Apr-Jun;43(2-3):75-80. Acta Virol. 1999. PMID: 10696424 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of interferon resistance mediated by viral-directed inhibition of PKR, the interferon-induced protein kinase.Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Apr;78(1):29-46. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(97)00165-4. Pharmacol Ther. 1998. PMID: 9593328 Review.
Cited by
-
The VP35 protein of Ebola virus inhibits the antiviral effect mediated by double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):182-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01006-06. Epub 2006 Oct 25. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17065211 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural analysis of ICP34.5- herpes simplex virus 1 replication in mouse brain cells in vivo.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):10982-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00337-10. Epub 2010 Aug 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20702618 Free PMC article.
-
Resources to Discover and Use Short Linear Motifs in Viral Proteins.Trends Biotechnol. 2020 Jan;38(1):113-127. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Trends Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31427097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the role of autophagy in replication of herpes simplex virus in cell culture.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(22):12128-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01356-07. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17855538 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora A kinase inhibition enhances oncolytic herpes virotherapy through cytotoxic synergy and innate cellular immune modulation.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 14;8(11):17412-17427. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14885. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28147331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreansky, S., L. Soroceanu, E. R. Flotte, J. Chou, J. M. Markert, G. Y. Gillespie, B. Roizman, and R. J. Whitley. 1997. Evaluation of genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses as oncolytic agents for human malignant brain tumors. Cancer Res. 57:1502-1509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

