Antisense Tcf inhibits the neoplastic growth of liver cancer cells
- PMID: 15221470
- PMCID: PMC12161790
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-004-0580-9
Antisense Tcf inhibits the neoplastic growth of liver cancer cells
Abstract
Purpose: T cell transcription factors are nuclear effectors of the Wnt signaling transduction pathway and play crucial roles in embryonic and malignant development. Our previous study showed increased expression level of Tcf mRNA in liver cancer. In the present paper, antisense Tcf RNA was used to explore the possible therapeutic effect on liver cancer cells by interrupting the abnormal Wnt pathway.
Methods: Antisense expression vectors containing the conserved sequence of Tcf cDNA were constructed and transfected into a human liver cancer cell line SMMC-7721. Tumorigenic potential was determined by cellular growth assay and tumor growth in nude mice.
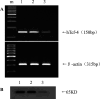
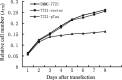
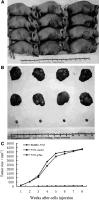
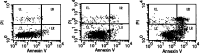
Results: The stable transfection of anti-sense Tcf in SMMC-7721 cells significantly reduced Tcf expression at both mRNA and protein levels compared with parental and mock-transfected cells. Antisense-mediated suppression of Tcf inhibited the in vitro proliferation and in vivo tumor formation ability. Furthermore, the apoptosis rate of antisense transfected cells was significantly higher than that of control, indicating that antisense RNA suppressed malignant growth by induction of apoptosis.
Conclusion: Our studies demonstrate the critical role of Wnt signaling pathway in the neoplastic growth of liver cancer cells and suggest that inhibition of Tcf activity with antisense Tcf RNA may be a potential new gene therapy method for liver cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of WNT10A in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its effect on cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 28;50(3):402-415. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240237. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40628509 Chinese, English.
-
Apoptosis of human BEL-7402 hepatocellular carcinoma cells released by antisense H-ras DNA--in vitro and in vivo studies.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1997;123(1):25-33. doi: 10.1007/BF01212611. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1997. PMID: 8996537 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
Cited by
-
Selection and Characterization of a Novel DNA Aptamer, Apt-07S Specific to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Apr 20;14:1535-1545. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S244149. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32368012 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy of liver cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Oct 14;12(38):6085-97. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6085. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17036377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of genes regulated by Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and involved in apoptosis via microarray analysis.BMC Cancer. 2006 Sep 7;6:221. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-221. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16959035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cadigan KM, Nusse R (1997) Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev 11:3286–3305 - PubMed
-
- Peifer M, Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis--a look outside the nucleus. Science 287:1606–1609 - PubMed
-
- Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 14:1837–1851 - PubMed
-
- Polakis P (2001) More than one way to skin a catenin. Cell 105:563–566 - PubMed
-
- Zeng L, Fagotto F, Zhang T, et al (1997) The mouse Fused locus encodes Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway that regulates embryonic axis formation. Cell 90:181–192 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

