Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for palliative treatment of portal hypertension secondary to portal vein tumor thrombosis
- PMID: 15222028
- PMCID: PMC4572222
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1881
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for palliative treatment of portal hypertension secondary to portal vein tumor thrombosis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the palliative therapeutic effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) complicated by portal hypertension.
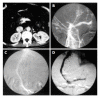
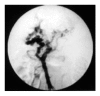
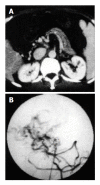
Methods: We performed TIPS for 14 patients with PVTT due to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Of the 14 patients, 8 patients had complete occlusion of the main portal vein, 6 patients had incomplete thrombosis, and 5 patients had portal vein cavernous transformation. Clinical characteristics and average survival time of 14 patients were analysed. Portal vein pressure, ascites, diarrhoea, and variceal bleeding and circumference of abdomen were assessed before and after TIPS.
Results: TIPS was successful in 10 cases, and the successful rate was about 71%. The mean portal vein pressure was reduced from 37.2 mmHg to 18.2 mmHg. After TIPS, the ascites decreased, hemorrhage stopped and the clinical symptoms disappeared in the 10 cases. The average survival time was 132.3 d. The procedure failed in 4 cases because of cavernous transformation in portal vein and severe cirrhosis.
Conclusion: TIPS is an effective palliative treatment to control hemorrhage and ascites due to HCC complicated by PVTT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with covered stents for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Feb 14;20(6):1602-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1602. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24587637 Free PMC article.
-
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for Portal Hypertension in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017 Sep;40(9):1372-1382. doi: 10.1007/s00270-017-1655-8. Epub 2017 May 9. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28488102
-
Combined transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and other interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal hypertension.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 21;21(43):12439-47. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12439. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26604651 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: portal vein recanalisation and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for portal vein thrombosis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jan;49(1):20-30. doi: 10.1111/apt.15044. Epub 2018 Nov 18. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30450634
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review.United European Gastroenterol J. 2023 Oct;11(8):733-744. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12454. Epub 2023 Sep 22. United European Gastroenterol J. 2023. PMID: 37736854 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) in Treating Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jun 15;59(6):1150. doi: 10.3390/medicina59061150. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37374354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fully Covered Stent-TIPS for Advanced HCC Patients with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus-Related Severe Symptomatic Portal Hypertension.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Jan 14;12:29-41. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S491153. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 39830160 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent thrombotic occlusion of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt due to activated protein C resistance.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Aug 28;11(32):5064-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.5064. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16124068 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Perioperative Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Primary Hepatic Carcinoma.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 29;2022:9000331. doi: 10.1155/2022/9000331. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9838954. doi: 10.1155/2023/9838954. PMID: 35815267 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of trans-jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for cirrhotic patients with portal vein thrombosis.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jul 6;9(19):5179-5190. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5179. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34307565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papatheodoridis GV, Goulis J, Leandro G, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt compared with endoscopic treatment for prevention of variceal rebleeding: A meta-analysis. Hepatology. 1999;30:612–622. - PubMed
-
- Xu K, Zhang HG, He XF, Zhao ZC, Ren K, Jin CY, Han MJ, Wang CL. Preliminary report on portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt: analysis of 8 cases. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 1993;27:294–297.
-
- Zhang JS, Wang MQ, Yang L. [Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts] Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 1994;74:150–152. - PubMed
-
- Wang MQ, Zhang JS, Gao YA. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt: an experimental study. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 1993;28:324–327.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

