Role of mitochondria in cell apoptosis during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effect of ischemic postconditioning
- PMID: 15222040
- PMCID: PMC4572234
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1934
Role of mitochondria in cell apoptosis during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effect of ischemic postconditioning
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the role of mitochondria in cell apoptosis during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effect of ischemic postconditioning (IPC).
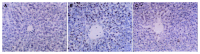
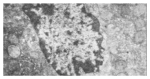
Methods: A rat model of acute hepatic ischemia-reperfusion was established, 24 healthy male Wistar rats were randomly divided into sham-operated group, ischemia-reperfusion group (IR) and IPC group. IPC was achieved by several brief pre-reperfusions followed by a persistent reperfusion. Concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA) and activity of several antioxidant enzymes in hepatic tissue were measured respectively. Apoptotic cells were detected by TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) and expression of Bcl-2 protein was measured by immunohistochemical techniques. Moreover, mitochondrial ultrastructure and parameters of morphology of the above groups were observed by electron microscope.
Results: Compared with IR group, the concentration of MDA and the hepatocellular apoptotic index in IPC group was significantly reduced (P<0.05), while the activity of antioxidant enzymes and OD value of Bcl-2 protein were markedly enhanced (P<0.05). Moreover, the injury of mitochondrial ultrastructure in IPC group was also obviously relieved.
Conclusion: IPC can depress the synthesis of oxygen free radicals to protect the mitochondrial ultrastructure and increase the expression of Bcl-2 protein that lies across the mitochondrial membrane. Consequently, IPC can reduce hepatocellular apoptosis after reperfusion and has a protective effect on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Figures


References
-
- Oshiro T, Shiraishi M, Muto Y. Adenovirus mediated gene transfer of antiapoptotic protein in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury: the paradoxical effect of Bcl-2 expression in the reperfused liver. J Surg Res. 2002;103:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Chen MF, Chen JC, Chiu DF, Ng CJ, Shyr MH, Chen HM. Prostacyclin analogue (OP-2507) induces delayed ex vivo neutrophil apoptosis and attenuates reperfusion-induced hepatic microcirculatory derangement in rats. Shock. 2001;16:473–478. - PubMed
-
- Sileri P, Schena S, Morini S, Rastellini C, Pham S, Benedetti E, Cicalese L. Pyruvate inhibits hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation. 2001;72:27–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

