Reversal of 5-flouroucial resistance by adenovirus-mediated transfer of wild-type p53 gene in multidrug-resistant human colon carcinoma LoVo/5-FU cells
- PMID: 15222051
- PMCID: PMC4572245
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1979
Reversal of 5-flouroucial resistance by adenovirus-mediated transfer of wild-type p53 gene in multidrug-resistant human colon carcinoma LoVo/5-FU cells
Abstract
Aim: To observe the reversal effects of wide-type p53 gene on multi-drug resistance to 5-FU (LOVO/5-FU).
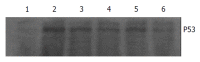
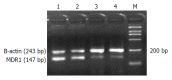
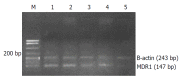
Methods: After treatment with Ad-p53, LOVO/5-FU sensitivity to 5-Fu was investigated using tetrazolium dye assay. Multidrug resistance gene-1 (MDR1) gene expression was assayed by semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and the expression of p53 protein was examined by Western blotting.
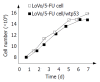
Results: The reversal activity after treatment with wide-type p53 gene was increased up to 4.982 fold at 48 h. The expression of MDR1 gene decreased significantly after treatment with wide-type p53 gene, and the expression of p53 protein lasted for about 5 d, with a peak at 48 h, and began to decrease at 72 h.
Conclusion: Wide-type p53 gene has a remarkable reversal activity for the high expression of MDR1 gene in colorectal cancers. The reversal effects seem to be in a time dependent manner. It might have good prospects in clinical application.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of adenovirus expressing wild-type p53 on 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity is related to p53 status in pancreatic cancer cell lines.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Dec 15;10(24):3583-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3583. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15534911 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects and Mechanisms of Periplaneta americana Extract Reversal of Multi-Drug Resistance in BEL-7402/5-FU Cells.Molecules. 2016 Jun 28;21(7):852. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070852. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27367657 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of phosphatase and tensin homology deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) gene transfection on reversal of multidrug resistance in K562/ADM cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Jul;53(7):1383-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.650695. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22185283
-
[Correlation of chemosensitivity measured by histoculture drug response assay to expression of multidrug resistance genes and proteins in gastric cancer].Ai Zheng. 2009 Apr;28(4):337-43. Ai Zheng. 2009. PMID: 19622290 Chinese.
-
Synergistic anticancer effect of exogenous wild-type p53 gene combined with 5-FU in human colon cancer resistant to 5-FU in vivo.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 28;22(32):7342-52. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7342. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27621580 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic strategies targeting Wnt/β‑catenin signaling for colorectal cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Jan;49(1):1. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5056. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34713301 Free PMC article.
-
p53 and metabolism: from mechanism to therapeutics.Oncotarget. 2018 May 4;9(34):23780-23823. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25267. eCollection 2018 May 4. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29805774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Mechanisms Accounting for the Refractoriness of Colorectal Carcinoma to Pharmacological Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 11;12(9):2605. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092605. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32933095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mir-148a improves response to chemotherapy in sensitive and resistant oesophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma cells.J Gastrointest Surg. 2011 Mar;15(3):429-38. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1418-9. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011. PMID: 21246413
-
5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies.Molecules. 2008 Aug 5;13(8):1551-69. doi: 10.3390/molecules13081551. Molecules. 2008. PMID: 18794772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhu XH, Li JY, Xia XM, Zhu MQ, Geng MJ, Chen L, Zhang JQ. [Multidrug resistance mechanisms in cell line HL-60/VCR] Ai Zheng. 2002;21:1310–1313. - PubMed
-
- Tsuruo T. Molecular cancer therapeutics: recent progress and targets in drug resistance. Intern Med. 2003;42:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Fromm MF. The influence of MDR1 polymorphisms on P-glycoprotein expression and function in humans. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54:1295–1310. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Smyth MJ. Multiple physiological functions for multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:1–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

